Menu
Physics Lesson 19.5.1 - Recalling the Simple Harmonic Wave (Oscillation)
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Recalling the Simple Harmonic Wave (Oscillation), this is the first lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Recalling the Simple Harmonic Wave (Oscillation)
We know that the position (in two dimensions) of any point of a standing wave is expressed through the sinusoidal equation of simple harmonic motion, that is
where
y(t) is the y-coordinate of a given point of a wave at any instant t,
x is the x-coordinate of the given point of wave (it is up to us to choose any point we want, so the x-coordinate depends on our choice),
t is the time instant in which we are interested to know the position of the given point of wave,
ω = 2π · f is the angular frequency of wave, and
k = 2π/λ is the wave number - a feature that depends only on the wavelength.
Thus, the above equation can also be written as
The shape of the simple harmonic wave in two dimensions is shown below.
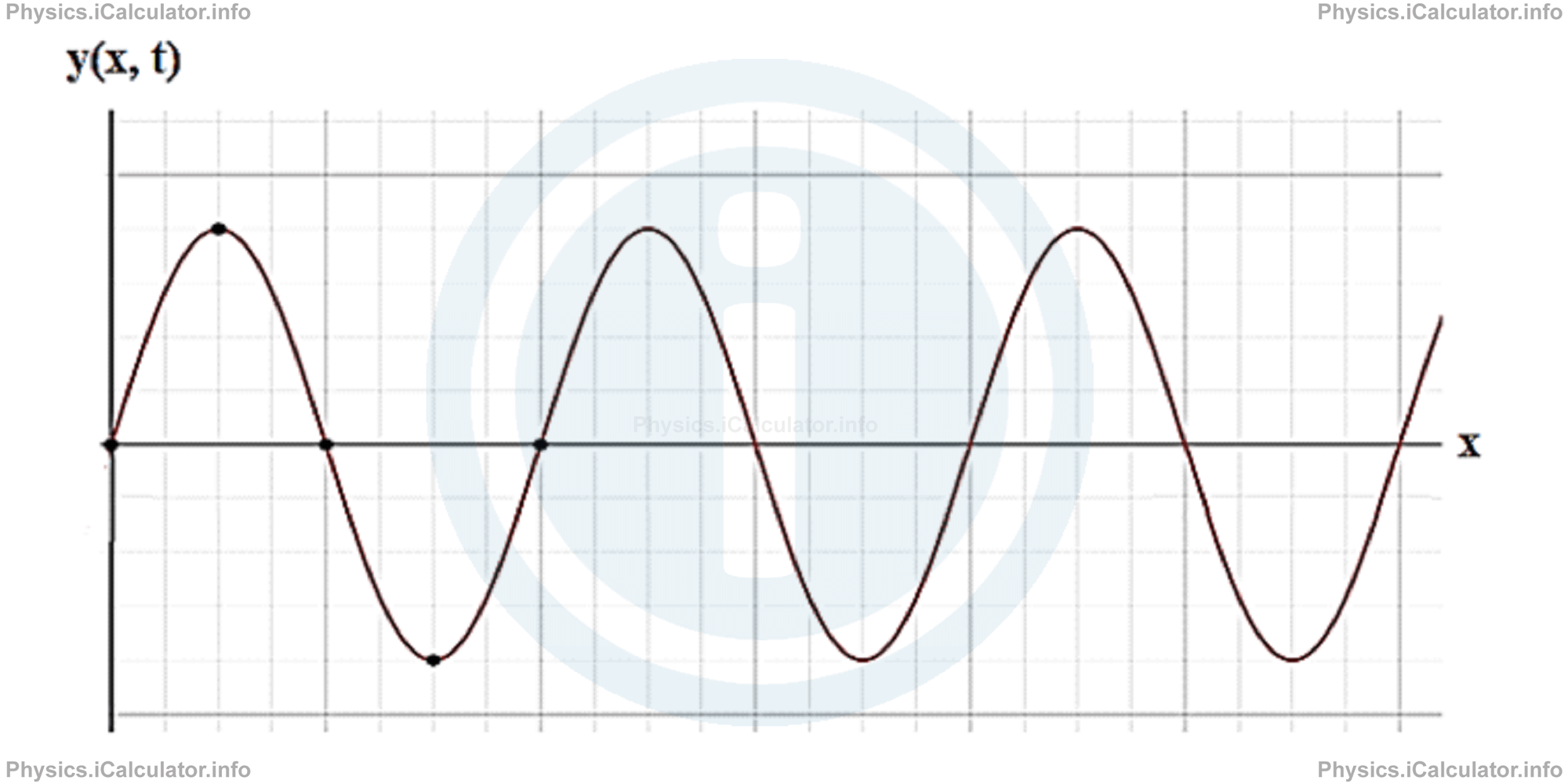
For simple harmonic waves, frequency is determined by the features of emitting source, hence it can be considered as constant. The same for wavelength if the wave is propagating in a homogenous medium (where the wave speed is the same throughout the entire medium), given the equation of waves
Such waves (with constant frequency) are emitted from sources that oscillate unceasingly in a periodic fashion. In these conditions, the wave would propagate in space up to infinity (ideal or standing waves). Obviously, in the real world this cannot occur, as the environment will eventually drain up the wave's energy. However, if we consider short intervals of time up to few minutes, many real waves behave in a similar way as ideal waves. For example, a sound source, a radio emitter etc., can be described using the standing wave pattern.
The approach is different when considering the oscillation of atoms, molecules or other microscopic particles however. Despite they represent EM sources too, their radiation is discrete (with interruptions). A single radiating action produced by atoms is very short; it lasts a few nanoseconds (1 ns = 10-9 s). Therefore, when studying the radiation of atoms, we always refer to "wave packets" instead of individual waves. Likewise, photons are also emitted in wave packets.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 19.5.1 Recalling the Simple Harmonic Wave (Oscillation). There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Recalling the Simple Harmonic Wave (Oscillation)" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle lesson found the following resources useful:
- Oscillation Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this oscillation (see below)
- Modern Physics Physics tutorial: Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle. Read the Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Modern Physics
- Modern Physics Revision Notes: Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle
- Modern Physics Practice Questions: Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle. Test and improve your knowledge of Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Modern Physics questions with our excellent Modern Physics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Modern Physics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning modern physics - read our next physics tutorial: Thermal Radiation. Photon as the Quantum of Light
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Modern Physics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Characteristic Em Wavelength Calculator
- De Broglie Wave Calculator
- Rayleigh Jeans Relation Calculator
- Energy Of Photons Calculator
- Intensity Photoelectric Effect Calculator
- Kinetic Photoelectric Effect Calculator
- Light Pressure Calculator
- Radiation Black Body Calculator
- Stopping Voltage Photoelectric Effect Calculator
- Uncertainty Calculator
- Wave Width Calculator
- Scattered Radiation Compton Effect Calculator
- De Broglie Packet Calculator