Menu
Physics Lesson 19.5.2 - Definition and Features of Wave Packet
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Definition and Features of Wave Packet, this is the second lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Definition and Features of Wave Packet
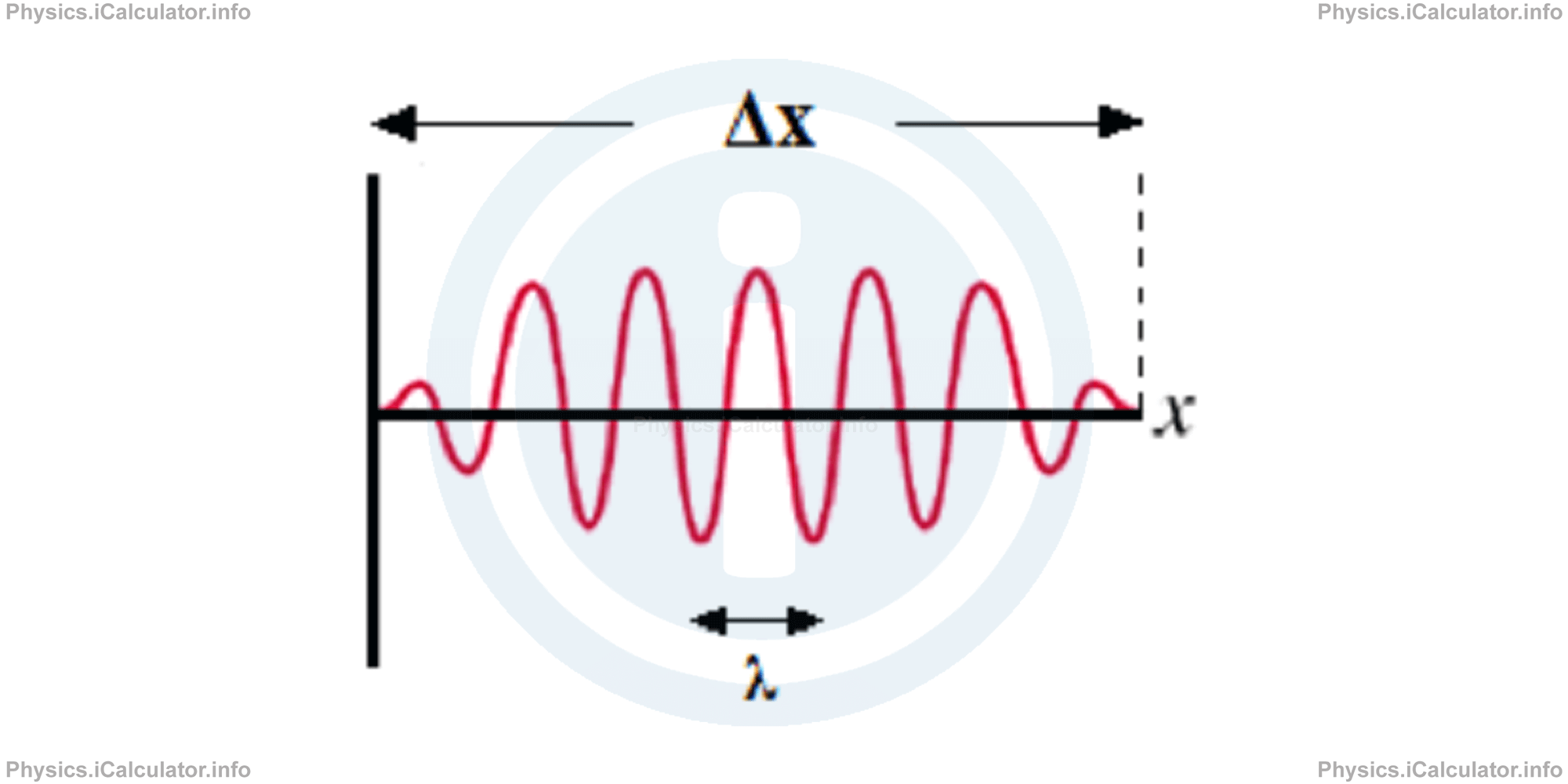
A "wave packet" is a fragmented or a discrete wave. It represents a short or a burst wave All sources that operate periodically in short intervals emit wave packets. Therefore, a wave packet has a limited width in space. The spatial extension Δx of a wave packet is given by the equation
where v is the packet's speed and Δτ is the time interval between two consecutive emissions.
Example 1
Calculate the spatial extension of a radio-wave packet emitted by an AC source in any country in Europe.
Solution 1
Clues:
(v = c = 300 000 km/s = 3 × 108 m/s)
Δx = ?
We know that the frequency of all AC sources in Europe is f = 50 Hz. Therefore, the source oscillates in time intervals of
This value corresponds to the time interval between two consecutive emissions from the source. Thus, we have
= 2 × 10-2 s
Hence, since the spatial extension of a wave packet is given by
we obtain after substitutions:
= c ∙ ∆τ
= (3 × 108 m/s) ∙ (2 × 10-2 s)
= 6 × 106 m
= 6000 km
Since the extension of this packet is very large, we can consider this wave as an ideal standing wave.
Now, let's consider another example but this time, the wave source is an atom.
Example 2
Calculate the spatial extension achieved by a photon emitted by an atom during the time interval of 10-9 s.
Solution 2
Clues:
Δτ = 10-9 s
(c = 3 × 108 m/s)
Δx = ?
Giving that
we obtain after substitutions:
= c ∙ ∆τ
= (3 × 108 m/s ∙ (10-9 s)
= 0.3 m
From the result, you can see that the EM wave packets emitted by atoms are very concentrated. This allows us visualize the photon as a particle.
Advanced theoretical calculations show that any wave packet does not contain a single a single wavelength but an infinite number of wavelengths instead. These values range from λ - λ/2 to λ + λ/2, where λ represents the mean wavelength of wave packet. The width Δλ of such wave packets relates to its spatial extension through the relation:
This relation is characteristic for any wave group or packet, whose shape is shown in the figure below.
Example 3
Calculate the wave width of a photon and compare it to the mean wavelength (λ = 600 nm) given that its spatial extension is Δx ≈ 0.3 m.
Solution 3
Clues:
Δλ = ?
Δx = 0.3 m
λ = 600 nm = 6 × 10-7 m
Applying the equation
we find for the wave width Δλ after substituting the known values:
= (6 × 10-7 m)2/2 ∙ 3.14 ∙ (0.3 m)
= 1.91 × 10-13 m
This result means the wave width of photon is much shorter (about 300 000 times shorter) than its average wavelength. This results in an almost continuous type of photons emission, which makes the identification of the discrete nature of light very difficult.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 19.5.2 Definition and Features of Wave Packet. There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Definition and Features of Wave Packet" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle lesson found the following resources useful:
- Defintion Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this defintion (see below)
- Modern Physics Physics tutorial: Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle. Read the Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Modern Physics
- Modern Physics Revision Notes: Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle
- Modern Physics Practice Questions: Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle. Test and improve your knowledge of Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Modern Physics questions with our excellent Modern Physics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Modern Physics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning modern physics - read our next physics tutorial: Thermal Radiation. Photon as the Quantum of Light
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electromagnetic Wave Packet. The Uncertainty Principle" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Modern Physics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Characteristic Em Wavelength Calculator
- De Broglie Wave Calculator
- Rayleigh Jeans Relation Calculator
- Energy Of Photons Calculator
- Intensity Photoelectric Effect Calculator
- Kinetic Photoelectric Effect Calculator
- Light Pressure Calculator
- Radiation Black Body Calculator
- Stopping Voltage Photoelectric Effect Calculator
- Uncertainty Calculator
- Wave Width Calculator
- Scattered Radiation Compton Effect Calculator
- De Broglie Packet Calculator