Menu
Physics Lesson 12.6.3 - Types of Polarization
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Types of Polarization, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Polarization of Light, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Types of Polarization
There are three types of light polarization: linear, circular and elliptic. Let's explain the features of each of them.
a) Linear polarization
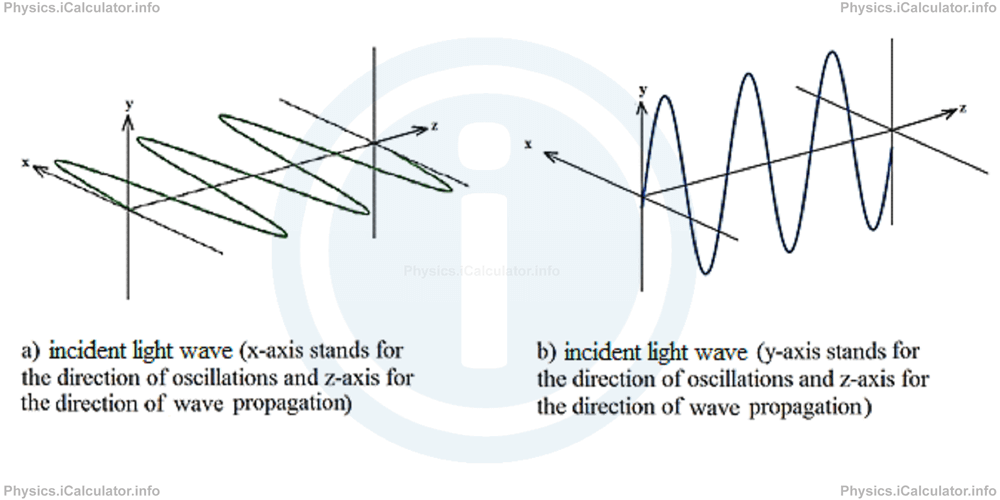
In this type of polarization, the electric field is confined to a single plane. This means we obtain a 2-D wave from the original 3-D one. It is called linear polarization because the electric vector oscillates only in one dimension (the other dimension stands for the direction of wave propagation). Look at the figure below in which two incident waves at right angle (one oscillates in the x direction and the other in the y-direction while both propagating in the z-direction) are shown.
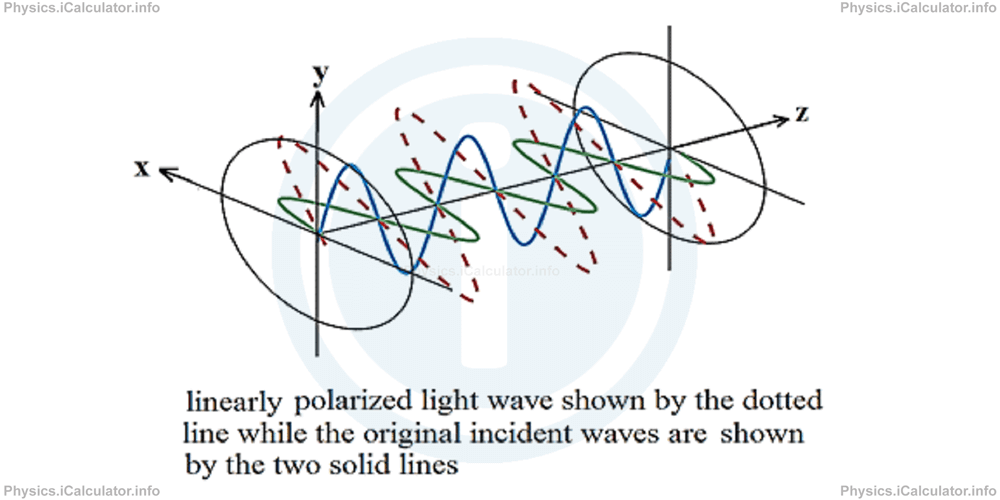
After polarization occurs, the oscillation of polarized wave will have a different angle from each single original wave as shown in the figure below, in which the polarized light wave is shown through the dotted line.
The direction of polarized wave changes continuously; thus, at another instant, the polarized wave pattern will be like this:
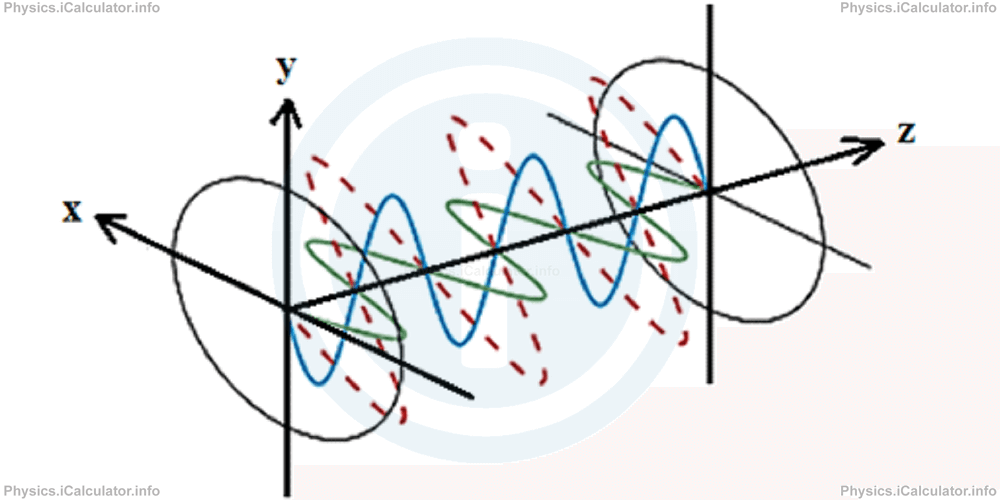
Linear polarization occurs when the two incident waves oscillate at 900 between them but they don't have any phase difference, i.e. they are at phase.
b) Circular Polarization
In this kind of polarization the incident waves still have a 900 oscillating direction between them. However, unlike in linear polarization, these incident waves have a phase shift of π/2 between them. As a result, they form a circular polarized wave pattern as shown in the figure.
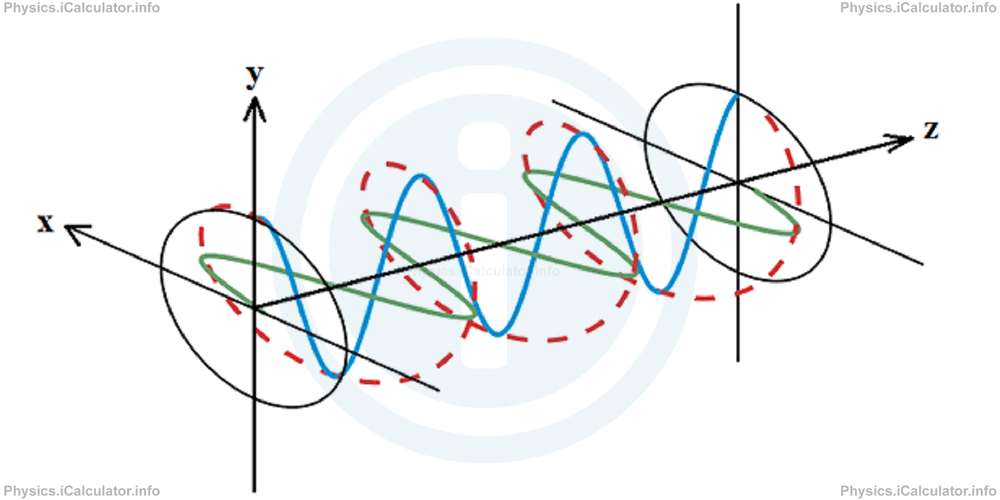
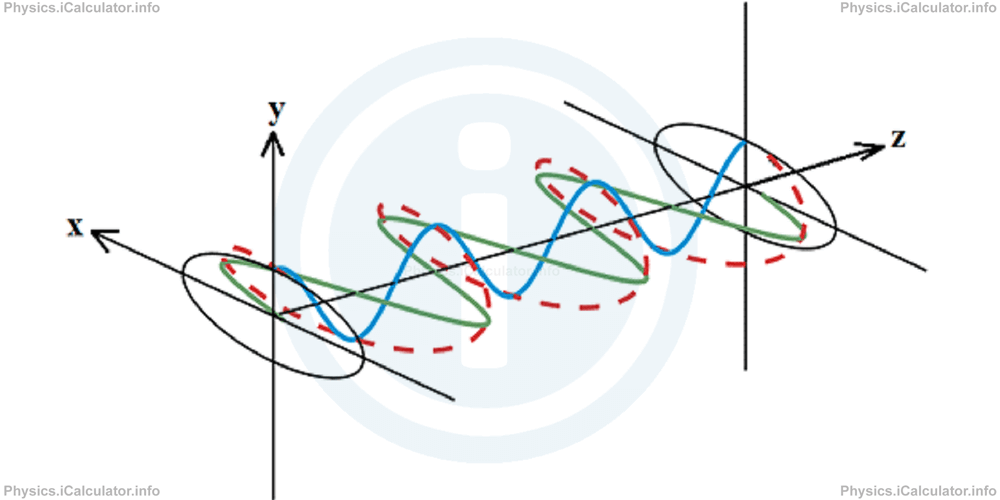
Therefore, we can say if the two incident waves oscillate according the x and y directions respectively and if one wave is displaced at maximum position when the second one is at the equilibrium position, a circular pattern is produced when polarization occurs. It is true that this circular pattern occurs according the xOy plane, but since all waves propagate in the z-direction, a spring-like pattern is produced in the polarized wave as shown by the dotted line in the above figure.
c) Elliptic Polarization
Elliptic polarization occurs in two conditions:
- when the amplitudes of the incident waves are not equal, or
- when the angle between the oscillation direction (i.e. of electric vector) of the two incident waves is not 900.
In this case, an elliptic pattern for the polarized wave is produced. Look at the figure.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.6.3 Types of Polarization. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Polarization of Light, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Polarization of Light Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Types of Polarization" physics lesson? People who liked the "Polarization of Light lesson found the following resources useful:
- Types Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this types (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Polarization of Light. Read the Polarization of Light physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Polarization of Light. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Polarization of Light
- Optics Practice Questions: Polarization of Light. Test and improve your knowledge of Polarization of Light with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: The Doppler Effect
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Polarization of Light" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.