Menu
Physics Lesson 12.6.2 - What is Polarization of Light?
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on What is Polarization of Light?, this is the second lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Polarization of Light, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
What is Polarization of Light?
As discussed in the Physics tutorial on the Features of Light, EM waves have two components - one electric and the other magnetic -, which oscillate at right angles to each other. However, since the magnetic component of light is much smaller than the electric one (it is smaller by a factor of 3 × 108, i.e. equal to the speed of light in vacuum), we consider only the electric component of EM radiation when dealing with the wave behaviour of light.
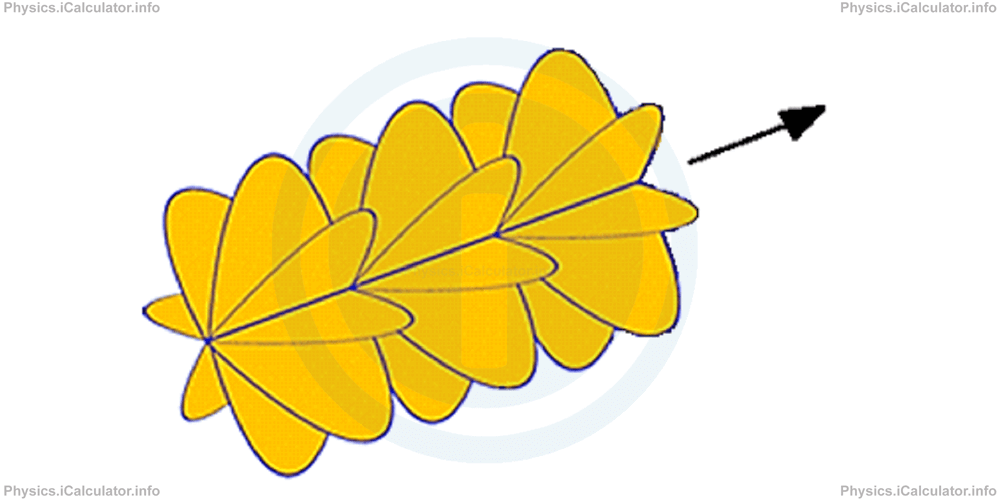
However, this description of EM waves' pattern is very helpful in understanding how waves of different wavelength contained in a single beam oscillate in respect to each other. It is proved that light waves oscillate at different angles (depending on their colours) to each other despite propagating through the same axis as shown in the figure.
When we place a coloured glass in the light path, all colours are absorbed by the glass (as explained in the previous paragraph), except one colour - the colour of the glass. In this way, the coloured glass acts like a barrier to the other waves and it allows to pass through only one light wave - the wave that has the same colour to it. This property is known as polarization of light. By definition,
Polarization of light is the restriction of the electric vector oscillation in a single direction (or in simpler words, the restriction of the light wave in a single plane).
This means all the other directions of light oscillation are eliminated except one, as shown in the figure below.
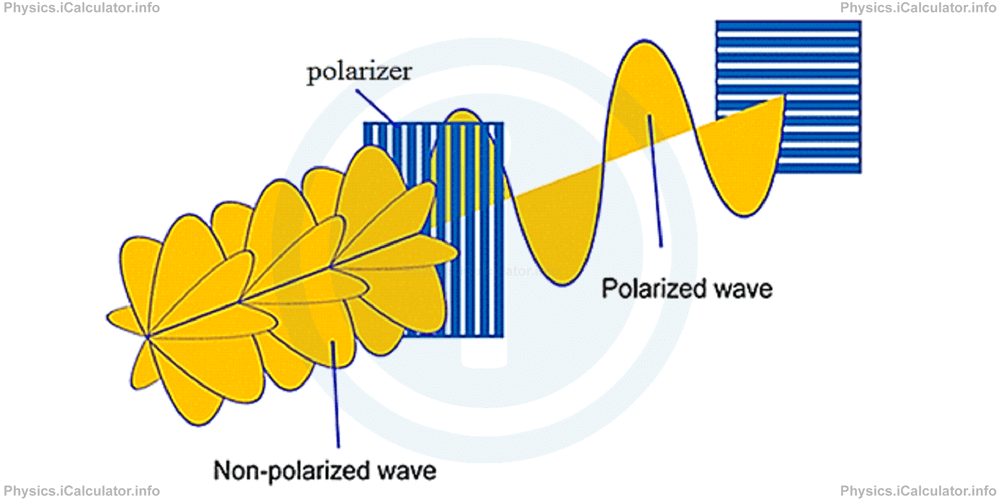
The coloured glass can be substituted by a transparent glass in which parallel gratings at a distance from each other (which is smaller than the waves amplitude) are made. In this case, gratings act like jail bars, i.e. they don't allow the light waves that do not oscillate according their direction to pass through. This kind of glass is known as polarizer.
When we put another polarizer at right angle to the first one, the light is completely blocked as it cannot pass longwise through the narrow gratings as shown in the figure above.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.6.2 What is Polarization of Light?. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Polarization of Light, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Polarization of Light Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "What is Polarization of Light?" physics lesson? People who liked the "Polarization of Light lesson found the following resources useful:
- Definition Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this definition (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Polarization of Light. Read the Polarization of Light physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Polarization of Light. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Polarization of Light
- Optics Practice Questions: Polarization of Light. Test and improve your knowledge of Polarization of Light with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: The Doppler Effect
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Polarization of Light" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.