Menu
Physics Lesson 12.6.6 - Malus Law
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Malus Law, this is the sixth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Polarization of Light, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Malus Law
Non-polarized light can be considered as a continuous switch between p and s polarizations. If we take an ideal linear polarizer for simplicity, it is clear that such a polarizer will transmit only one type of polarization at a time. Therefore, the intensity of polarized light will be half of that of the original light. Thus, if we denote the initial intensity of unpolarised light by I0 and the intensity of polarized light by î(both measured in candela, [cd] which is one of the seven fundamental Sîunits), we obtain
To describe the relationship between polarized light I, unpolarised light I0 and the angle θ between the incident linear polarization and the polarization axis, we use the so-called Malus Law:
Example 1
Calculate the light intensity of the polarized light if the parallel lines of the reflective linear polarizer used for this purpose form an angle of 300 to the electric vector of the incident light. Take the intensity of incident light equal to 20 cd, cos 300 = √3/2 and sin 300 = 1/2 if needed.
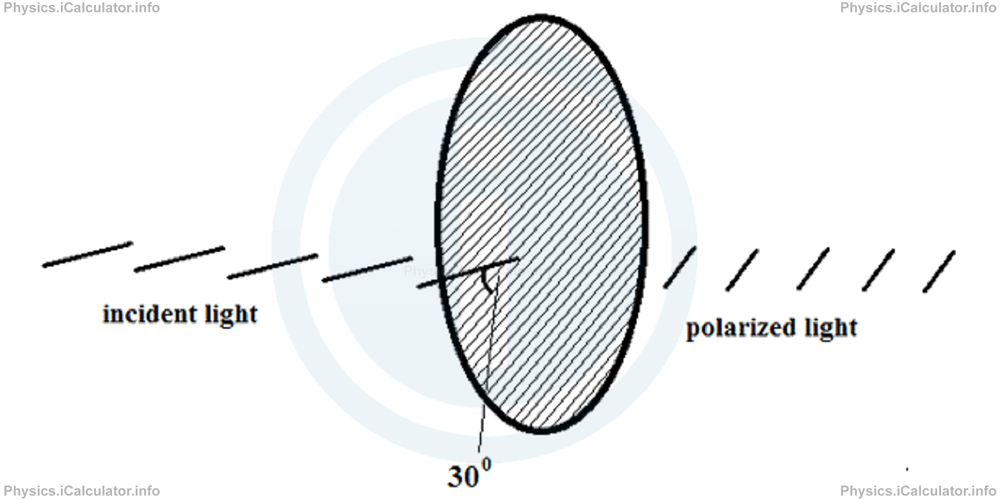
Solution 1
Applying the Malus Law
we obtain after substituting the values:
= 20 × √3/22
= 20 × 3/4
= 15 cd
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.6.6 Malus Law. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Polarization of Light, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Polarization of Light Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Malus Law" physics lesson? People who liked the "Polarization of Light lesson found the following resources useful:
- Malus Law Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this malus law (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Polarization of Light. Read the Polarization of Light physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Polarization of Light. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Polarization of Light
- Optics Practice Questions: Polarization of Light. Test and improve your knowledge of Polarization of Light with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: The Doppler Effect
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Polarization of Light" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.