Menu
Physics Lesson 16.6.4 - Magnetic Field Inside a Long Straight Wire with Current
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Magnetic Field Inside a Long Straight Wire with Current, this is the fourth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Ampere's Law, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Magnetic Field Inside a Long Straight Wire with Current
In this case, the radius r of Amperian loop is smaller than the radius R of wire. This means the Amperian loop is taken inside the wire's section. 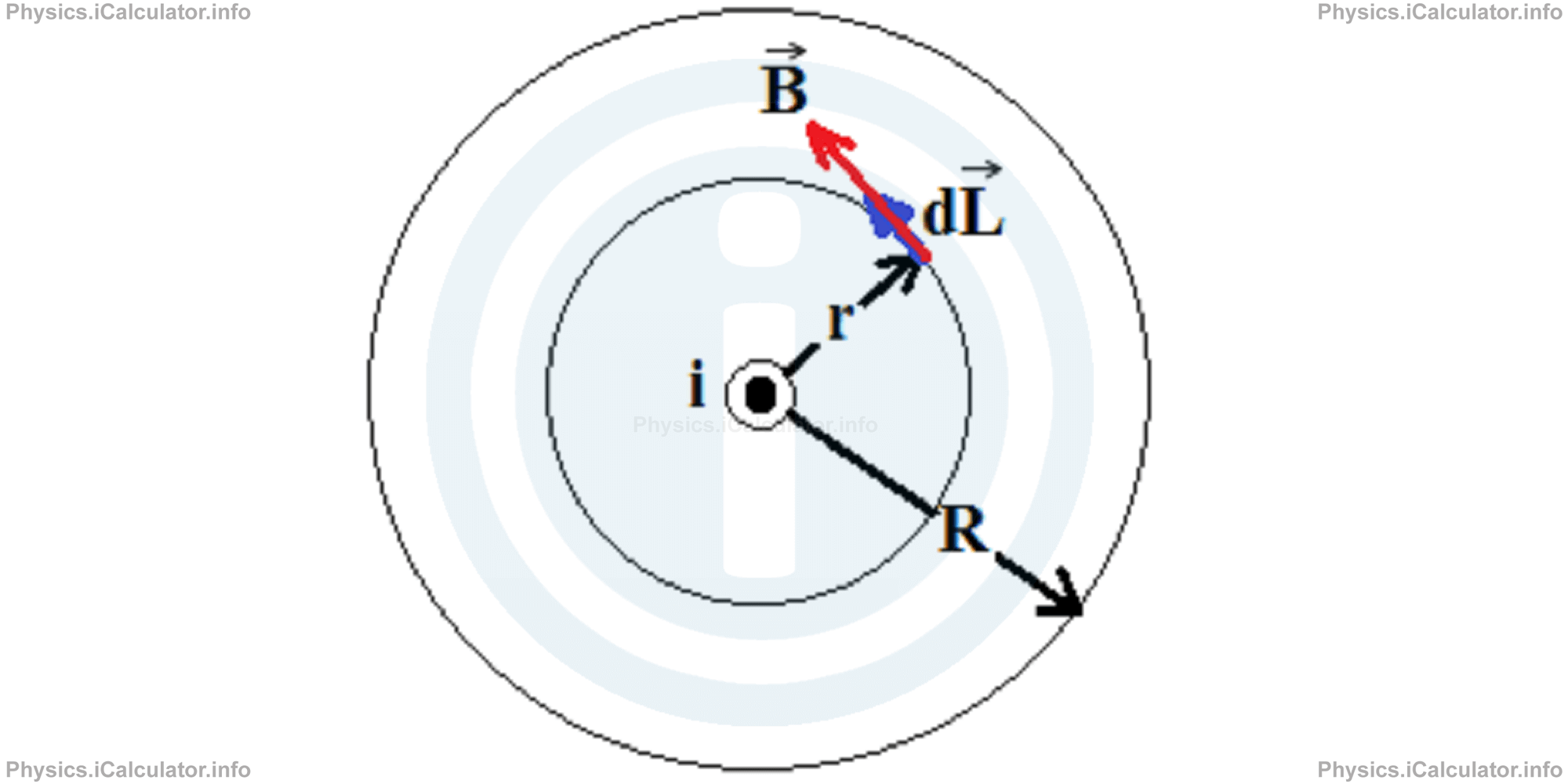
Like in the previous paragraph, the distribution of magnetic field has a cylindrical symmetry as the current is uniformly distributed throughout the wire (the direction is out of page). Therefore, we use a similar approach as in the calculation of magnetic field outside the wire discussed in the previous paragraph.
Using Ampere's law for this situation, we obtain for r < R:
= B ∙ ∮dL
= B ∙ (2π ∙ r)
= μ0 ∙ iencl
Since the current distribution is uniform, the current enclosed in the loop is proportional to the area of loop at any point, i.e.
or
Substituting this value for current in the previous formula obtained after integrating Ampere's law equation, yields
or
The above formula means the magnetic field is zero at centre of cross section of the wire and it has a maximum value for r = R (on the outer surface of wire). This is another proof that the electric charges (that are responsible for the magnetic field generation) are concentrated on the outer layer of conductor, as we have explained in Section 14.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 16.6.4 Magnetic Field Inside a Long Straight Wire with Current. There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Ampere's Law, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Ampere's Law Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Magnetic Field Inside a Long Straight Wire with Current" physics lesson? People who liked the "Ampere's Law lesson found the following resources useful:
- Inside Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this inside (see below)
- Magnetism Physics tutorial: Ampere's Law. Read the Ampere's Law physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Magnetism
- Magnetism Revision Notes: Ampere's Law. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Ampere's Law
- Magnetism Practice Questions: Ampere's Law. Test and improve your knowledge of Ampere's Law with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Magnetism questions with our excellent Magnetism calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Magnetism Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning magnetism - read our next physics tutorial: Faraday's Law of Induction
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Ampere's Law" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Magnetism Calculators by iCalculator™
- Angular Frequency Of Oscillations In Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Calculating Magnetic Field Using The Amperes Law
- Capacitive Reactance Calculator
- Current In A Rl Circuit Calculator
- Displacement Current Calculator
- Electric Charge Stored In The Capacitor Of A Rlc Circuit In Damped Oscillations Calculator
- Electric Power In A Ac Circuit Calculator
- Energy Decay As A Function Of Time In Damped Oscillations Calculator
- Energy Density Of Magnetic Field Calculator
- Energy In A Lc Circuit Calculator
- Faradays Law Calculator
- Frequency Of Oscillations In A Lc Circuit Calculator
- Impedance Calculator
- Induced Emf As A Motional Emf Calculator
- Inductive Reactance Calculator
- Lorentz Force Calculator
- Magnetic Dipole Moment Calculator
- Magnetic Field At Centre Of A Current Carrying Loop Calculator
- Magnetic Field In Terms Of Electric Field Change Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Long Stretched Current Carrying Wire Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Toroid Calculator
- Magnetic Field Produced Around A Long Current Carrying Wire
- Magnetic Flux Calculator
- Magnetic Force Acting On A Moving Charge Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Magnetic Force Between Two Parallel Current Carrying Wires Calculator
- Magnetic Potential Energy Stored In An Inductor Calculator
- Output Current In A Transformer Calculator
- Phase Constant In A Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Power Factor In A Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Power Induced On A Metal Bar Moving Inside A Magnetic Field Due To An Applied Force Calculator
- Radius Of Trajectory And Period Of A Charge Moving Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Self Induced Emf Calculator
- Self Inductance Calculator
- Torque Produced By A Rectangular Coil Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Work Done On A Magnetic Dipole Calculator