Menu
Physics Lesson 15.5.3 - Kirchhoff's Voltage Law
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Kirchhoff's Voltage Law, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Kirchhoff Laws, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law
The discussion above regarding currents behaviour is not sufficient to find the missing quantities in a circuit. We must also know what happens to the potential differences (voltages) in each component and how they are related to the electromotive forces produced by the sources. This information can be obtained using the Kirchhoff's Second Law (Kirchhoff's Voltage Law). It is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in a closed path (loop) adapted for voltages. The Kirchhoff's Second (Voltage) Law states that
The algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero.
This law is true because a circuit loop is a closed conducting path and therefore, no energy is lost. The charge flowing through a closed loop is also constant. Recall the relationship between electric potential energy and potential difference
The mathematical form of the Kirchhoff's Voltage Law is
Ohm's Law is just a special case of Kirchhoff's Law of Voltages because in a single resistor and single source circuit (if not considering the resistances of wire and source) we have
The Kirchhoff Law of Voltages is particularly useful when there is more than source in a single branch, especially when they are connected in opposite directions as shown in the first figure of this paragraph. Let's illustrate it with numbers to understand this point.
Example 4
What is the current flowing in the circuit below? Do not consider the resistance of wire and that of battery.
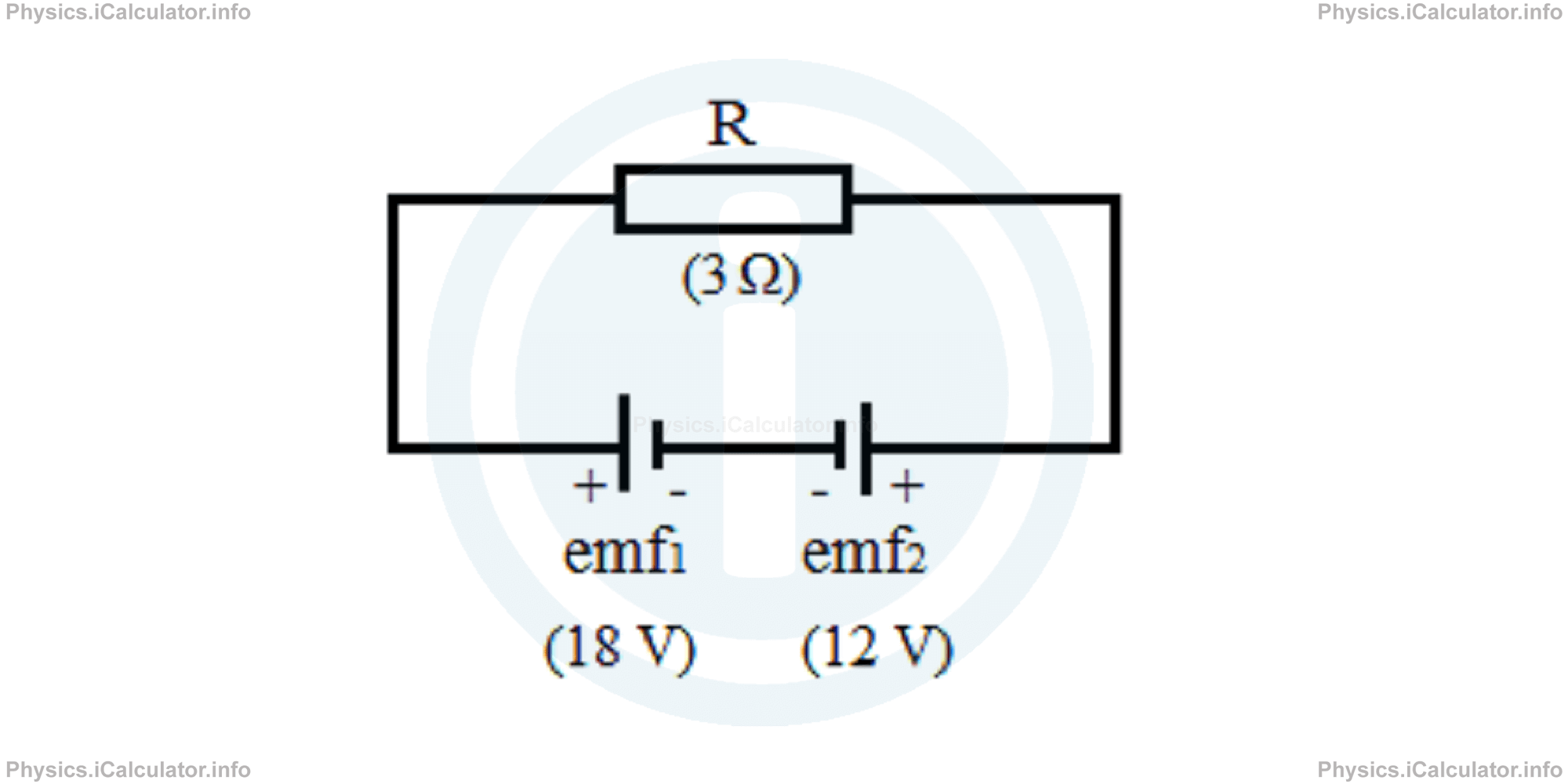
Solution 4
The first thing to do is to determine the direction of current flow as the two sources produce currents in opposite directions. Given that the first battery produces a higher current, we choose the clockwise direction (the direction determined by the first battery) as the direction of current flow. Hence, we must assume the emf of the 12 V battery as negative, as it produces an anticlockwise current. Thus, we obtain
Therefore, we obtain for the current flowing in the circuit
= 18 V - 12 V/3 Ω
= 2 Ω
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 15.5.3 Kirchhoff's Voltage Law. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Kirchhoff Laws, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Kirchhoff Laws Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Kirchhoff's Voltage Law" physics lesson? People who liked the "Kirchhoff Laws lesson found the following resources useful:
- Voltage Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this voltage (see below)
- Electrodynamics Physics tutorial: Kirchhoff Laws. Read the Kirchhoff Laws physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrodynamics
- Electrodynamics Revision Notes: Kirchhoff Laws. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Kirchhoff Laws
- Electrodynamics Practice Questions: Kirchhoff Laws. Test and improve your knowledge of Kirchhoff Laws with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrodynamics questions with our excellent Electrodynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrodynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Power and Efficiency
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Kirchhoff Laws" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Electrodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Amount Of Substance Obtained Through Electrolysis Calculator
- Charge Density Calculator
- Electric Charge Stored In A Rc Circuit Calculator
- Electric Field In Terms Of Gauss Law Calculator
- Electric Power And Efficiency Calculator
- Electron Drift Velocity Calculator
- Equivalent Resistance Calculator
- Force Produced By An Electric Source Calculator
- Joules Law Calculator
- Ohms Law Calculator
- Potential Difference In Rc Circuit Calculator
- Resistance Due To Temperature Calculator
- Resistance Of A Conducting Wire Calculator