Menu
Physics Lesson 15.1.3 - Direct Current. The Direction of Current Flow
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Direct Current. The Direction of Current Flow, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Current. Current Density, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Direct Current. The Direction of Current Flow
Direct current (DC) is the simplest type of current. The main producers of direct current are batteries, whose positive and negative terminals are well defined. This means the current has a single direction of flow throughout an electrical circuit. In the early days of electricity discovery, it was thought that positive charges move from the positive to negative terminal of battery. However, with the discovery of electron, it was made clear that there are electrons the particles that flow through the conductor, not the positive charges (protons). However, by agreement between scientists, it was decided to keep the actual direction of motion (from positive to negative). This direction was called the "conventional direction of current flow" and it is opposite to the direction of electrons flow (which is from negative to positive terminal of battery). Let's consider an analogy to clarify this point.
Suppose there are four people and five chairs available in a certain column of a theatre hall. Initially the firs chair is free and the four people are sitting from the second to the fifth chair. When the person who is sitting on the second chair realizes that nobody is coming to sit on the first chair, stands up and moves there. Similarly, the person who is sitting to the third chair moves to the second chair that is left free from the previous person, and so on. This process continues until the last chair remains free, because all the four people present now occupy the first four chairs of the column.
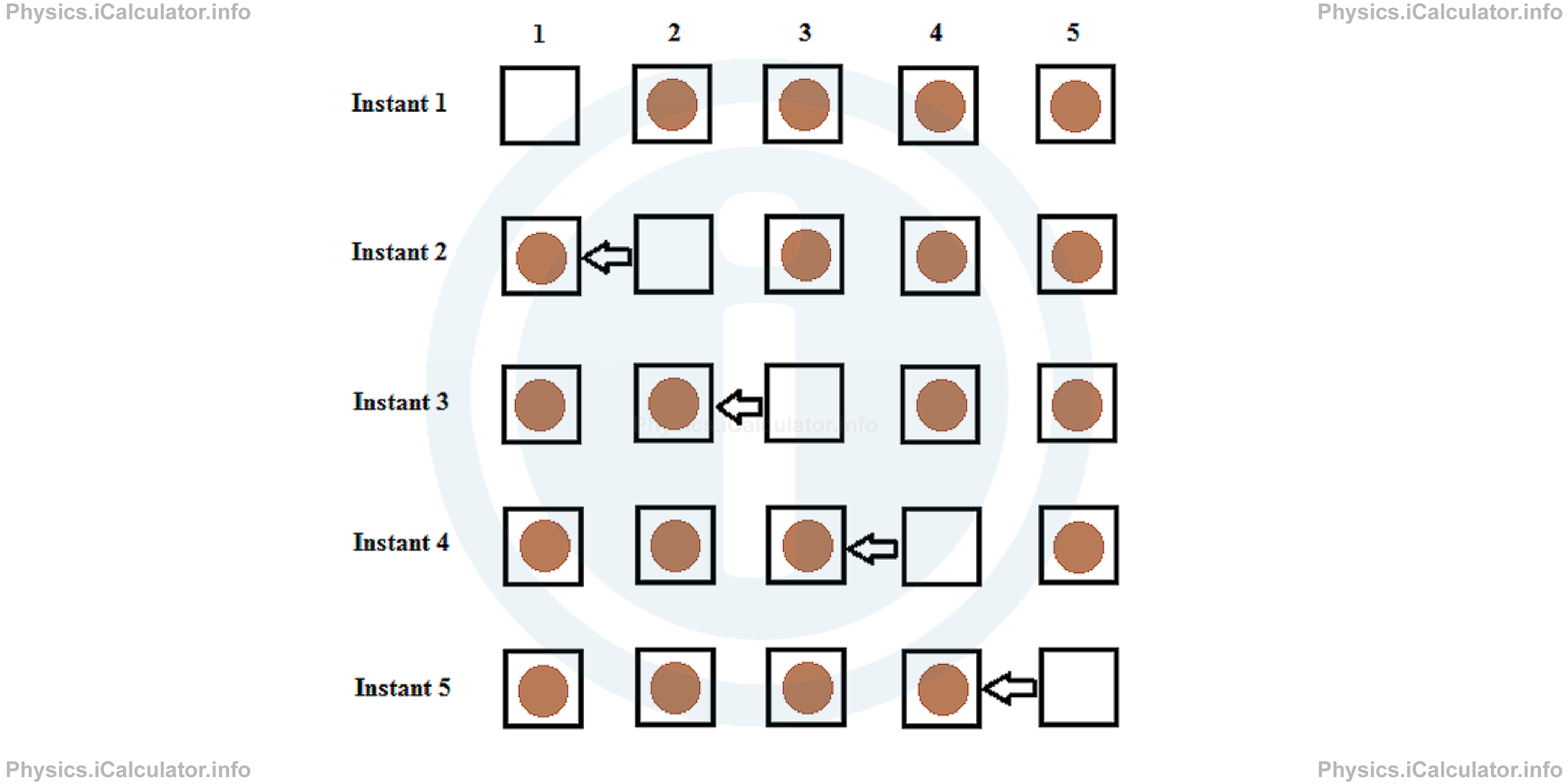
Thus, despite the true movement is the shift of a person by one position due left, it seems like an empty chair is shifting by one position due right. The stationary empty chairs here symbolize the positive charges (protons) while the moving people symbolize the electrons. Now, it is clear why we consider the direction of current from positive to negative despite electrons move in the opposite direction. After all, the result of calculations does not change.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 15.1.3 Direct Current. The Direction of Current Flow. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Current. Current Density, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Current. Current Density Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Direct Current. The Direction of Current Flow" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Current. Current Density lesson found the following resources useful:
- Direction Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this direction (see below)
- Electrodynamics Physics tutorial: Electric Current. Current Density. Read the Electric Current. Current Density physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrodynamics
- Electrodynamics Revision Notes: Electric Current. Current Density. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Current. Current Density
- Electrodynamics Practice Questions: Electric Current. Current Density. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Current. Current Density with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrodynamics questions with our excellent Electrodynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrodynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Resistance. Combinations of Resistors
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Current. Current Density" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Electrodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Amount Of Substance Obtained Through Electrolysis Calculator
- Charge Density Calculator
- Electric Charge Stored In A Rc Circuit Calculator
- Electric Field In Terms Of Gauss Law Calculator
- Electric Power And Efficiency Calculator
- Electron Drift Velocity Calculator
- Equivalent Resistance Calculator
- Force Produced By An Electric Source Calculator
- Joules Law Calculator
- Ohms Law Calculator
- Potential Difference In Rc Circuit Calculator
- Resistance Due To Temperature Calculator
- Resistance Of A Conducting Wire Calculator