Menu
Physics Lesson 12.1.4 - Visible Light Spectrum. Colours
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Visible Light Spectrum. Colours, this is the fourth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Features of Light, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Visible Light Spectrum. Colours
As explained earlier, humans can see EM waves of wavelength ranging from 400 nm to 700 nm. Shorter the wavelength, more powerful the wave. Our eyes perceive the strength of light waves through colours. Thus, the most powerful light waves we can see are of violet (purple) colour. This is the reason why UV radiation is the first category of EM waves that are more powerful than our ability to see ("ultra" means "beyond", i.e. ultraviolet rays means rays beyond the violet part of visible light spectrum).
Similarly, the weakest light rays we can see are of red colour as they are near the infrared part of EM spectrum (infra means "under" or "below", therefore infrared radiation means radiation that is below (less powerful than) the red part of visible light.
The order of colours from the least powerful to the most powerful (from the less energetic to the most energetic) is:
Red → Orange → Yellow → Green → Cyan → Blue → Violet
Look at the figure below.
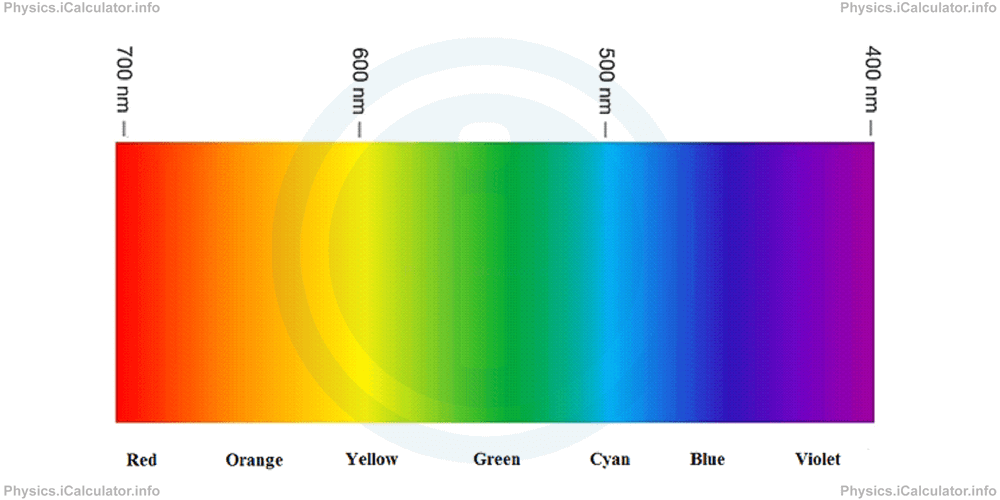
The following values give the range of wavelengths for each colour:
Red → 700 nm - 635 nm
Orange → 635 nm - 590 nm
Yellow → 590 nm - 560 nm
Green → 560 nm - 520 nm
Cyan → 520 nm - 490 nm
Blue → 490 nm - 450 nm
Violet → 450 nm - 400 nm
Obviously, there are no fixed borders between colours (the transition or switch between colours is gradual). Therefore, we must refer to values at middle of each range to be sure we have the colour we are looking for. This means we have some typical values for the wavelength of each colours, which represent them in exercises. For example, we can take 540 nm as typical wavelength for green light, 470 nm for blue light and so on.
Remark! The above values are valid for wavelengths of light waves in vacuum as when light passes through another medium it slows down and therefore the wavelengths decrease (frequency does not change).Example 1
A light wave has a frequency of 5.2 × 1014 Hz. What colour has this light wave?
Solution 1
From the equation of light waves
and given that c = 3 × 108 m/s, we obtain for the required wavelength
= 3 × 108/5.2 × 1014
= 0.577 × 10-6 m
= 577 × 10-9 m
= 577 nm
From the above list, it is obvious this light wave belongs to yellow part of visible light spectrum (590 nm - 560 nm).
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.1.4 Visible Light Spectrum. Colours. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Features of Light, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Features of Light Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Visible Light Spectrum. Colours" physics lesson? People who liked the "Features of Light lesson found the following resources useful:
- Spectrum Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this spectrum (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Features of Light. Read the Features of Light physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Features of Light. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Features of Light
- Optics Practice Questions: Features of Light. Test and improve your knowledge of Features of Light with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: Reflection of Light
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Features of Light" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.