Menu
Physics Lesson 12.1.6 - Shadows. Umbra and Penumbra
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Shadows. Umbra and Penumbra, this is the sixth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Features of Light, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Shadows. Umbra and Penumbra
Since light propagates in straight lines, it primarily illuminates objects that are in direct exposure to the light source. (We will see in the next section than objects are also illuminated indirectly through diffuse reflection, which helps us see objects that are not directly exposed to the light source). As a result, when we expose an opaque object to any light source, only the frontal side of the object, which is directly exposed to the light source, will be fully illuminated. Since opaque objects do not allow light rays to pass through them, the space behind such objects will be less illuminated. As a result, a dark region called shadow will exist in that part, as shown in the figure.
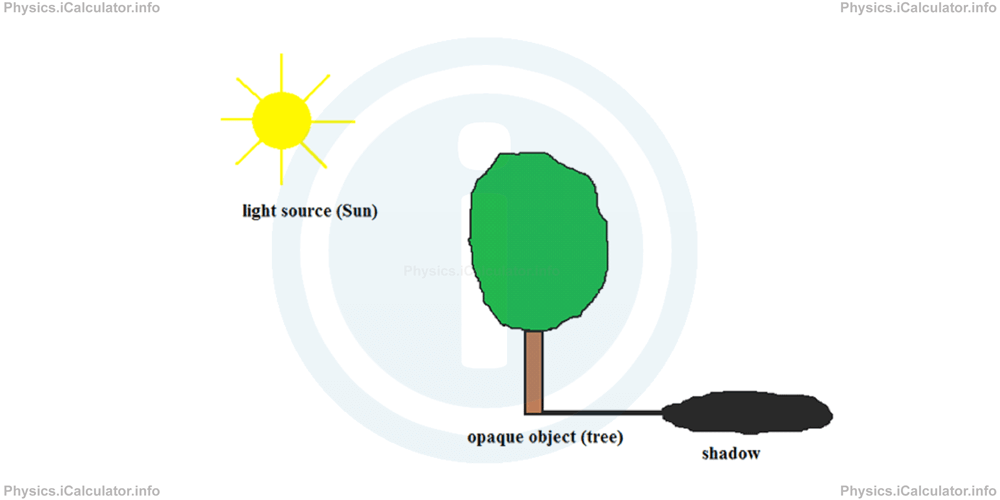
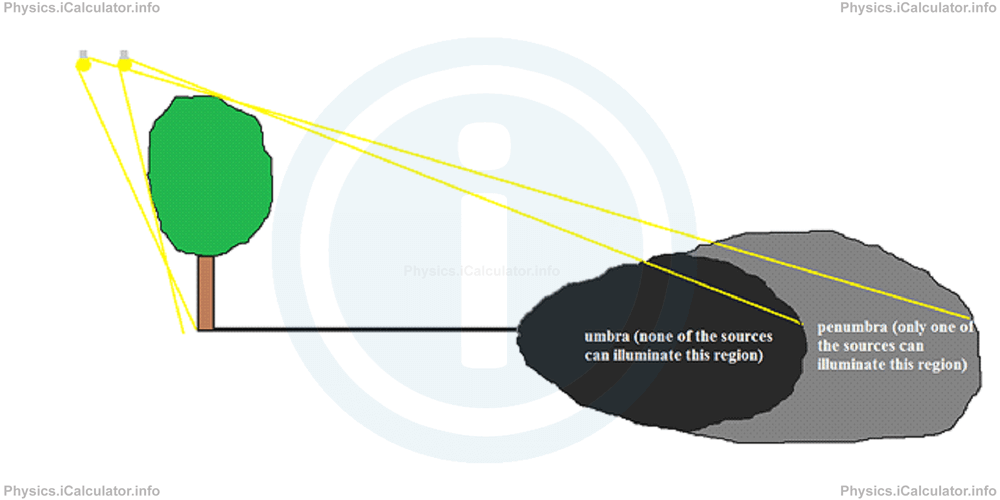
There are two types of shadows: umbra and penumbra. Umbra represents a complete shadow; it is formed when the light source is very small or when it is far away from the opaque objects (such as the Sun). In this case, an umbra is formed behind the object. Furthermore, the umbra borders are sharp, like in the above figure.
When the light source is relatively large and it cannot be considered as a point light source, or when there are two or more point sources emitting light, there will be regions behind an opaque object, which are partially illuminated. As a result, a dim shadow (half-shadow or penumbra) is formed on the ground in these regions as shown in the figure.
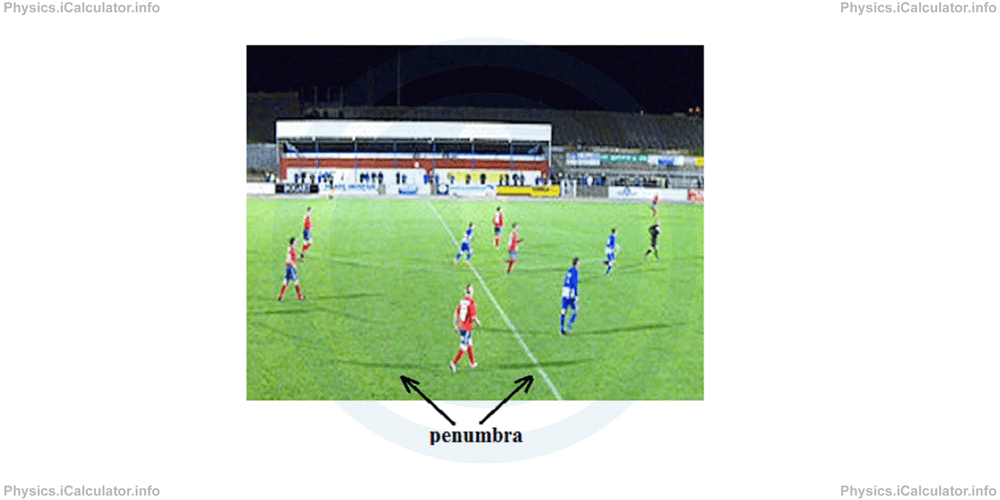
An example of penumbra is when you see a football match in the evening. The field is illuminated by multiple light sources. As a result, you see a number of dim shadows (penumbra) formed around the players because their opaque body blocks the light from one of sources but that part is illuminated by the other sources that are in different places around the field.
Example 2
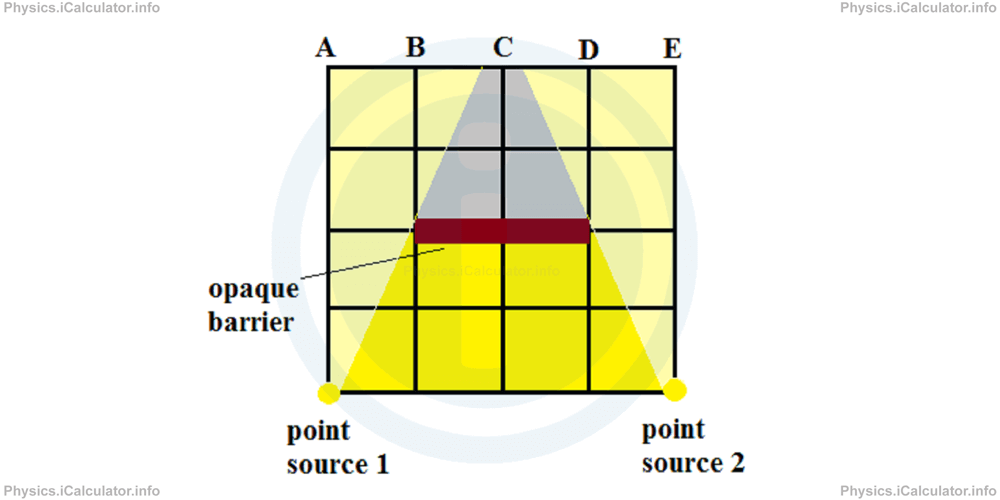
What kind of region (umbra, penumbra or illuminated) will form at the points A, B, C, D and E shown in the figure?
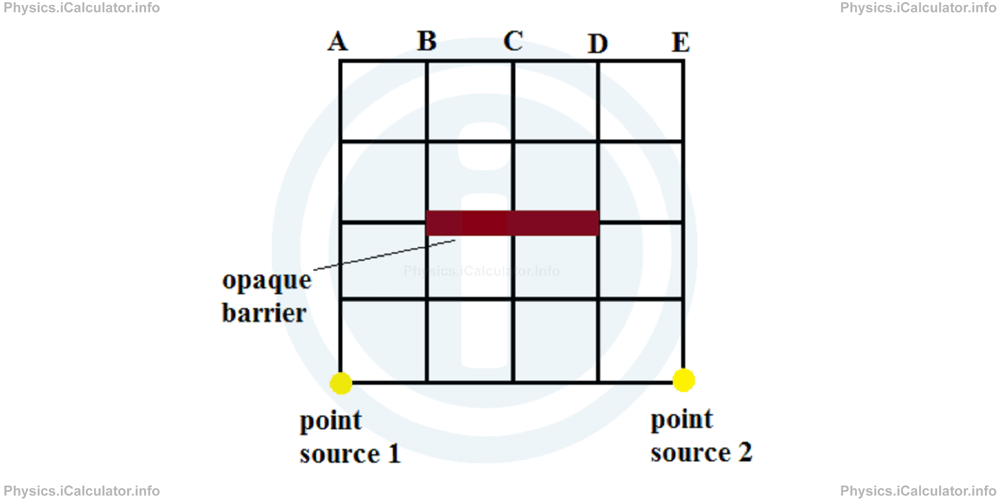
Solution 2
Points A and B are illuminated only by the source 1. Therefore, a penumbra is formed at these points.
Points D and E are illuminated only by the source 2. Therefore, a penumbra is formed at these points.
Point C is not illuminated by any source as the opaque barrier blocks the light emitted by them. Therefore, an umbra is formed at this point.
Look at the figure:
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.1.6 Shadows. Umbra and Penumbra. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Features of Light, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Features of Light Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Shadows. Umbra and Penumbra" physics lesson? People who liked the "Features of Light lesson found the following resources useful:
- Penumbra Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this penumbra (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Features of Light. Read the Features of Light physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Features of Light. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Features of Light
- Optics Practice Questions: Features of Light. Test and improve your knowledge of Features of Light with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: Reflection of Light
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Features of Light" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.