Menu
Physics Lesson 16.5.3 - Energy of a Magnetic Dipole
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Energy of a Magnetic Dipole, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Magnetic Dipole Moment, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Energy of a Magnetic Dipole
As we know from Section 5, objects and systems tend to occupy a state in which they have the lowest energy possible. For example, when you roll a ball inside a hole, it swings several times until it stops at bottom of the hole in which the ball is closer to the ground and therefore it has the lowest gravitational energy. Likewise, when you make a pendulum swing, it will stop at the vertical position, in which the bob is closer to the ground. In this case, the bob has the lowest gravitational potential energy possible. Another example: people lie on the bed when sleeping so that the centre of gravity of the body be as close as possible to the ground. In this case, they have the lowest energy possible and therefore, they can take a rest.
This rule is also true when a magnetic dipole is inserted inside an external magnetic field. When the vectors of magnetic field and magnetic dipole moment are collinear, the system has the lowest energy as the magnetic moment vector attempts to align with the magnetic field. Following this reasoning, we can say that when magnetic moment vector is antiparallel to the magnetic field lines (as in the previous solved example), the system has the highest energy possible.
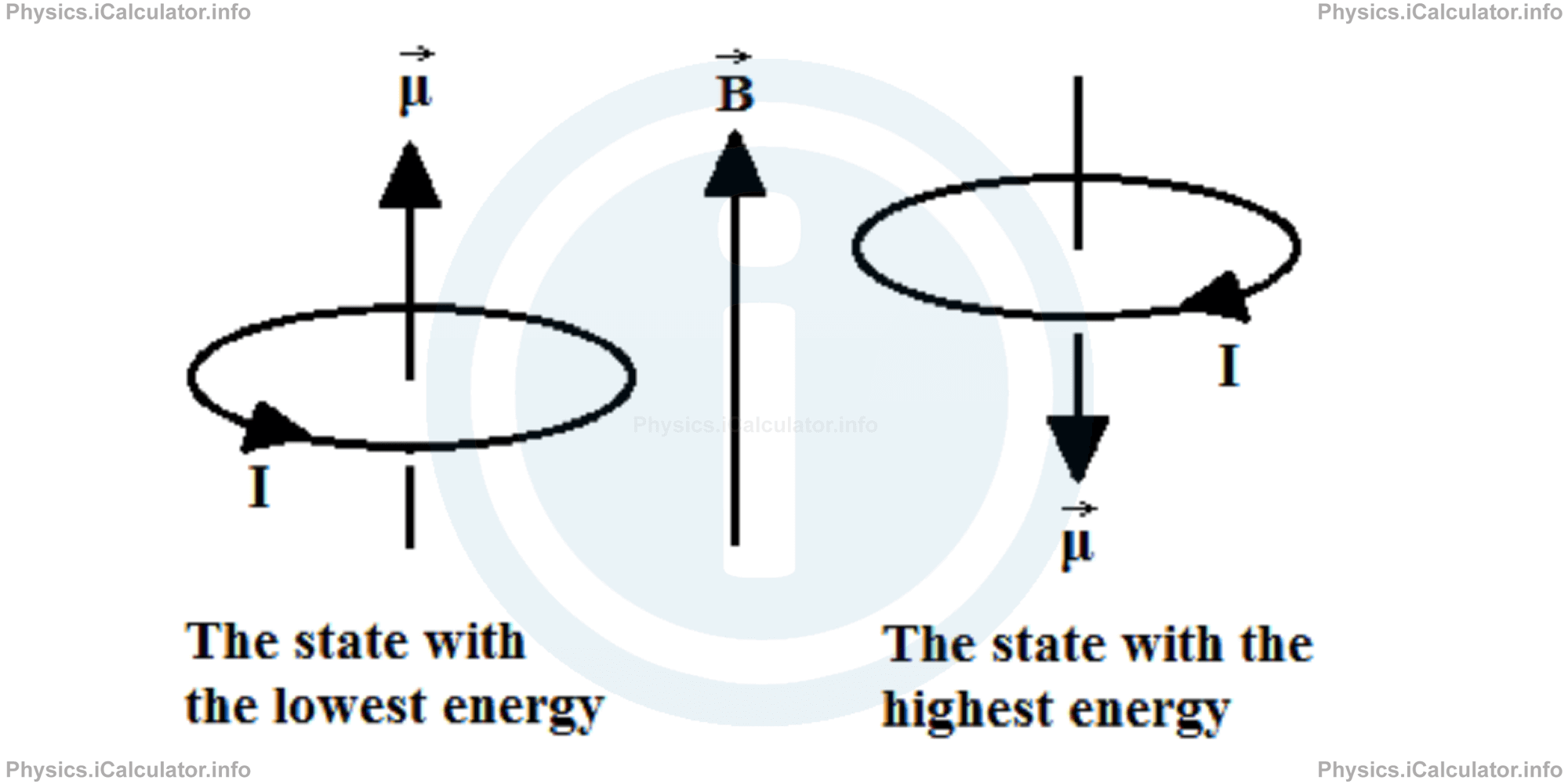
Therefore, we can say that a magnetic dipole in an external field has an energy that depends on the orientation of dipole moment in respect to the magnetic field direction. For electric dipoles, we have for the energy U in terms of the angle θ:
where p⃗ is the electric dipole moment and E⃗ is the electric field. Similarly, we obtain for the energy U of magnetic dipoles in terms of the angle θ:
Note that here we have a dot product of two vectors because energy is a scalar (the dot product of two vectors gives a scalar). The sign minus is because the maximum value of energy is obtained for θ = 180° for which cos θ = -1. In this way, we obtain a positive value for the maximum energy.
Example 3
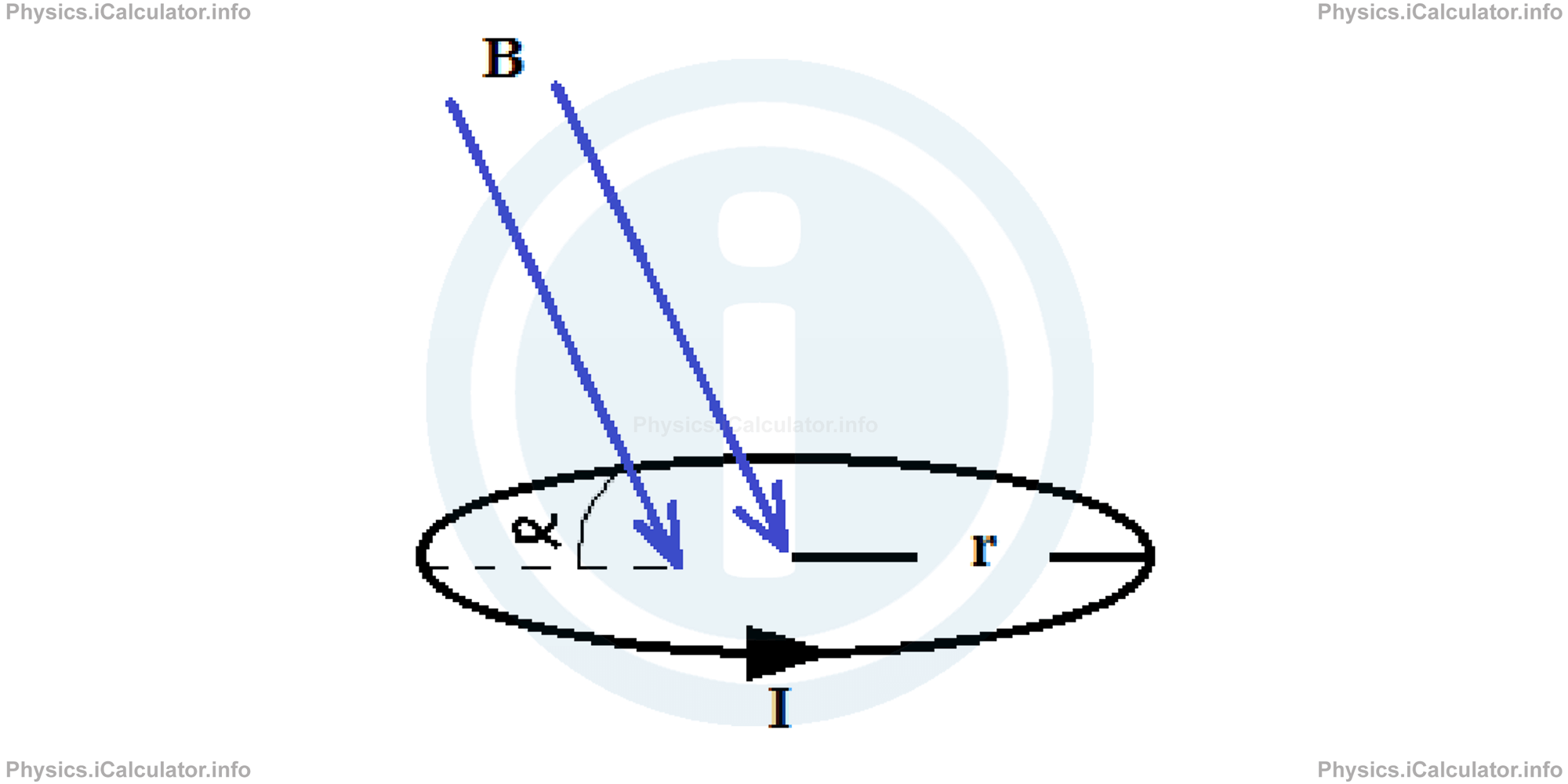
Calculate the energy of the magnetic dipole shown in the figure below if the radius of loop is r = 3cm, the current flowing through the loop is I = 5A and the magnetic field lines punch the area of loop at α = 60°. The magnitude of magnetic field is B = 40mT.
Solution 3
Clues:
r = 3 cm = 3 × 10-2 m
I = 5A
α = 600
B = 40 mT = 4 × 10-2 T
N = 1
U = ?
The vector of magnetic dipole moment is directed upwards. This is found using the right hand rule mentioned earlier.
The angle formed by the magnetic dipole moment vector to the magnetic field lines is θ = 90° + α = 90° + 60° = 150°.
The magnitude of magnetic dipole moment μ is
= N ∙ I ∙ π ∙ r2
= 1 ∙ (5A) ∙ 3.14 ∙ (3 × 10-2 m)2
= 1.413 × 10-2 A ∙ m2
The energy of the magnetic dipole therefore is
= -μ ∙ B ∙ cosθ
= -(1.413 × 10-2 A ∙ m2 ) ∙ (4 × 10-2 T) ∙ (cos1500 )
= -(1.413 × 10-2 A ∙ m2 ) ∙ (4 × 10-2 T) ∙ (-0.866)
= 4.89 × 10-4 J
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 16.5.3 Energy of a Magnetic Dipole. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Magnetic Dipole Moment, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Magnetic Dipole Moment Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Energy of a Magnetic Dipole" physics lesson? People who liked the "Magnetic Dipole Moment lesson found the following resources useful:
- Energy Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this energy (see below)
- Magnetism Physics tutorial: Magnetic Dipole Moment. Read the Magnetic Dipole Moment physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Magnetism
- Magnetism Revision Notes: Magnetic Dipole Moment. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Magnetic Dipole Moment
- Magnetism Practice Questions: Magnetic Dipole Moment. Test and improve your knowledge of Magnetic Dipole Moment with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Magnetism questions with our excellent Magnetism calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Magnetism Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning magnetism - read our next physics tutorial: Ampere's Law
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Magnetic Dipole Moment" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Magnetism Calculators by iCalculator™
- Angular Frequency Of Oscillations In Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Calculating Magnetic Field Using The Amperes Law
- Capacitive Reactance Calculator
- Current In A Rl Circuit Calculator
- Displacement Current Calculator
- Electric Charge Stored In The Capacitor Of A Rlc Circuit In Damped Oscillations Calculator
- Electric Power In A Ac Circuit Calculator
- Energy Decay As A Function Of Time In Damped Oscillations Calculator
- Energy Density Of Magnetic Field Calculator
- Energy In A Lc Circuit Calculator
- Faradays Law Calculator
- Frequency Of Oscillations In A Lc Circuit Calculator
- Impedance Calculator
- Induced Emf As A Motional Emf Calculator
- Inductive Reactance Calculator
- Lorentz Force Calculator
- Magnetic Dipole Moment Calculator
- Magnetic Field At Centre Of A Current Carrying Loop Calculator
- Magnetic Field In Terms Of Electric Field Change Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Long Stretched Current Carrying Wire Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid Calculator
- Magnetic Field Inside A Toroid Calculator
- Magnetic Field Produced Around A Long Current Carrying Wire
- Magnetic Flux Calculator
- Magnetic Force Acting On A Moving Charge Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Magnetic Force Between Two Parallel Current Carrying Wires Calculator
- Magnetic Potential Energy Stored In An Inductor Calculator
- Output Current In A Transformer Calculator
- Phase Constant In A Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Power Factor In A Rlc Circuit Calculator
- Power Induced On A Metal Bar Moving Inside A Magnetic Field Due To An Applied Force Calculator
- Radius Of Trajectory And Period Of A Charge Moving Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Self Induced Emf Calculator
- Self Inductance Calculator
- Torque Produced By A Rectangular Coil Inside A Uniform Magnetic Field Calculator
- Work Done On A Magnetic Dipole Calculator