Menu
Physics Lesson 13.1.1 - The Molecular Meaning of Temperature
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on The Molecular Meaning of Temperature, this is the first lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
The Molecular Meaning of Temperature
All particles of any object in whatever state it may be are in unceasing motion. In general, they vibrate around some fixed points known as "equilibrium positions". It is obvious that faster the particles' vibration, greater their kinetic energy.
It is impossible to measure the kinetic energy of all particles of an object due to the very big number of particles (but also because such motion is very irregular). Molecules of a objects may have a wide range of velocities, and furthermore, the speed of a molecule changes millions of times in a second due to the collisions with other molecules. At a given instant one molecule may nearly be at rest while another molecule moves with almost the speed of light during vibrations. Consequently, the kinetic energies of molecules of an object are quite different. But an average value of their kinetic energy gives us an idea about the behavior of an object's particles, especially in gases.
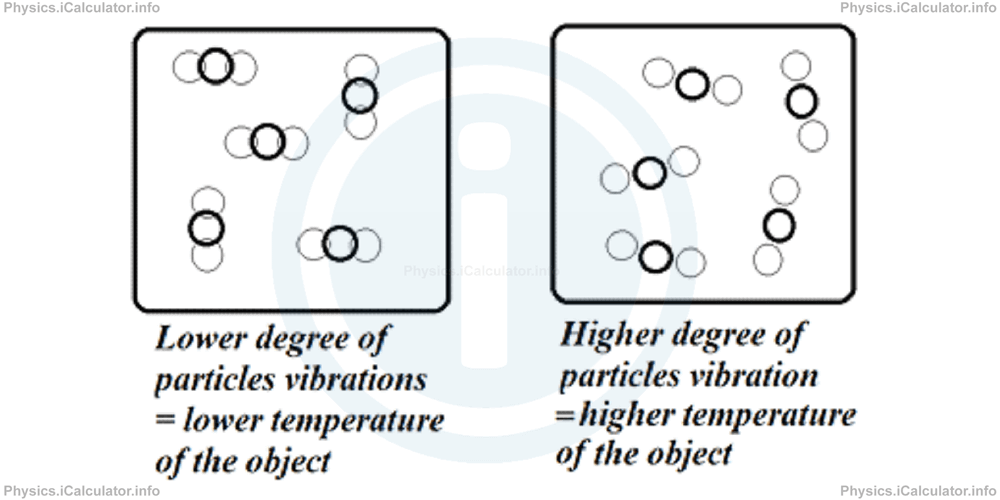
Therefore, we use an indirect way to estimate the kinetic energy of an object's particles (in other words its thermal energy), which is one of the main components of their internal energy (the other is the chemical energy generated during chemical reactions). The only way to draw a correct conclusion regarding the objects' degree of hotness is by finding an appropriate way to measure their warmth. This is achieved by introducing a more direct measurement than particles' average kinetic energy. As a result, a few centuries ago the concept of temperature was introduced.
By definition, temperature represents a measure of the ability of a substance, or more generally of any physical system, to transfer heat energy to another physical system.
Temperature as a concept is closely related to the average kinetic energy of all particles of the object or system. This means temperature is a more suitable quantity related to the measurements of objects' warmth than heat energy, because its value can be measured directly through devices called thermometers. A thermometer uses the expansive of contractive properties of liquids such as alcohol or mercury to show different values. But first, a thermometer needs to be graded. For this, a lower fixed point and an upper fixed point are needed. The process of assigning different values to different heights of liquid column in a thermometer is known as "calibration of thermometer".
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 13.1.1 The Molecular Meaning of Temperature. There are 3 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "The Molecular Meaning of Temperature" physics lesson? People who liked the "Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics lesson found the following resources useful:
- Definition Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this definition (see below)
- Thermodynamics Physics tutorial: Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. Read the Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics Revision Notes: Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics Practice Questions: Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. Test and improve your knowledge of Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Thermodynamics questions with our excellent Thermodynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Thermodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning thermodynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Thermal Expansion
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Temperature. The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Thermodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Carnot Engine Efficiency Calculator
- Entropy Calculator
- Gas Laws Calculator
- Molecular Mean Free Path Calculator
- Translational Kinetic Energy Of Gas Calculator
- Root Mean Square Speed Calculator
- Ideal Gas Law Calculator
- Change In The Gas Internal Energy Calculator
- Radiative Heat Transfer Calculator
- Evaporative Heat Transfer Calculator
- Convective Heat Transfer Calculator
- Conductive Heat Transfer Calculator
- Final Temperature Of Mixture Calculator
- Heat Absorbed Or Released Calculator
- Thermal Expansion Calculator
- Temperature Calculator