Menu
Physics Lesson 13.3.3 - States of Matter
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on States of Matter, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Absorption of Heat, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
States of Matter
Matter exists in three stable states: solid, liquid and gas. (Actually, there exist two other states of matter: plasma and Bose-Einstein particles, which are not stable, so in this tutorial we will focus only on the three abovementioned stable states.) Each of them has its own specific features which will be explained both in the visual and energetic viewpoint.
a) Solid State
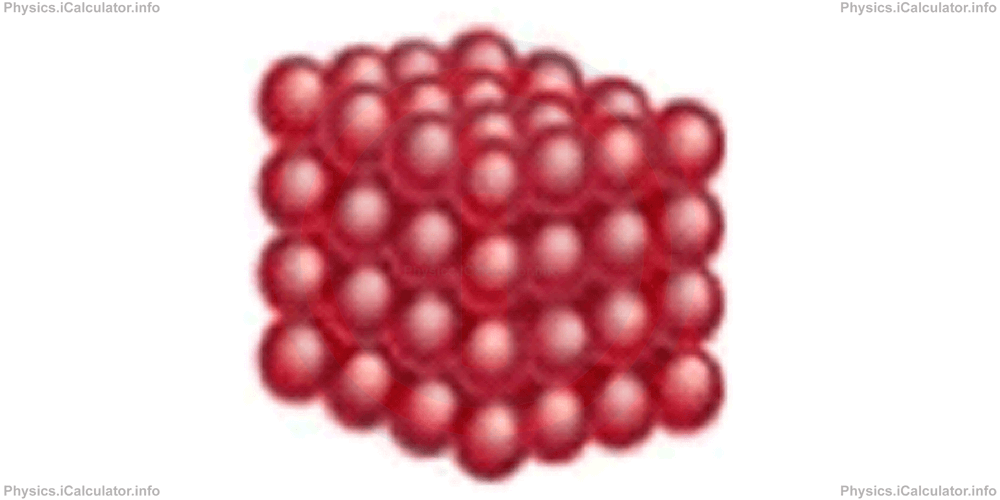
In solid state, particles are very close to each other. They are strongly bound to each other because the binding potential energy prevails over the kinetic energy of atoms. As a result, atoms can only vibrate around their equilibrium position but they cannot leave their predefined place. This means a certain atom in solid state has always the same "neighbours" around.
A cube in which some balls are placed at vertices and they are connected by each other by means of elastic springs, represents a very suitable pattern that helps us understand how solids work.
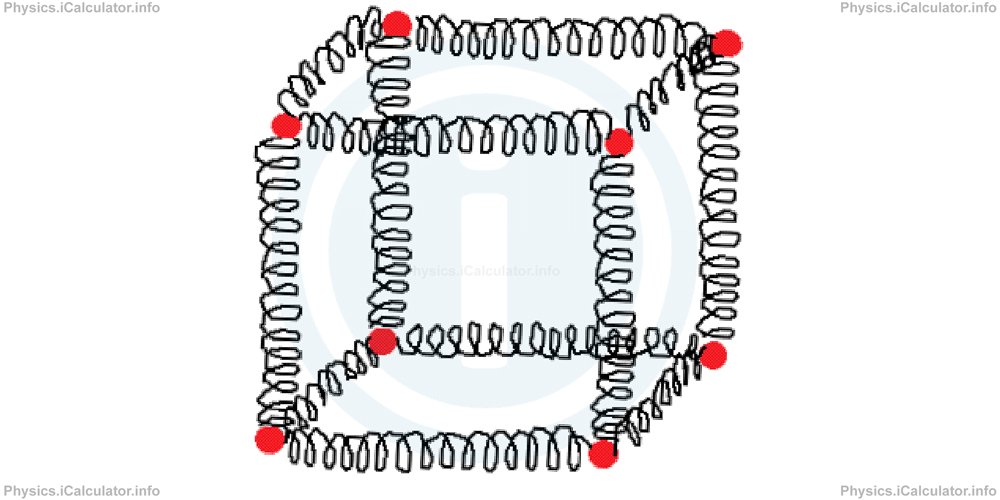
Thus, if we kick one of the balls, all balls will vibrate because the energy is spread out in every ball by means of the springs. The cube can rotate as a whole, but the balls cannot move from their positions. Likewise, the particles of a solid object will vibrate if some heat energy is supplied to one part of the object. It can shift, rotate, swing etc., as a whole, but the structure of the object will remain unchanged.
The structure of a solid object looks like the one shown in the figure below.
b) Liquid State
In liquid state, the particles slide over each other, as they are not so tightly bound. The atoms potential energy is still greater than their kinetic energy, so atoms still stay together. It is like opening a sack full of tennis-table balls and spread them throughout the room. The balls will slide over each other forming horizontal layers as shown in the figure.
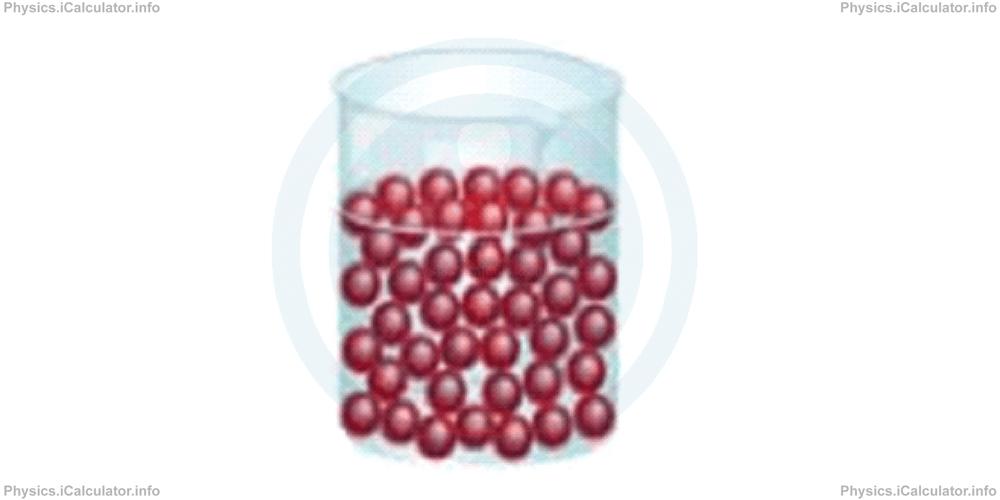
A liquid takes the shape of the container it is poured. Therefore, we can calculate the volume of a liquid by taking the volume of the container up to the liquid's level.
c) Gaseous State
In gaseous state, atoms are far away from each other; they move freely in space, as the atoms kinetic energy is greater than their potential energy. A gas fills the whole space of the container it is poured, as shown in the figure below.
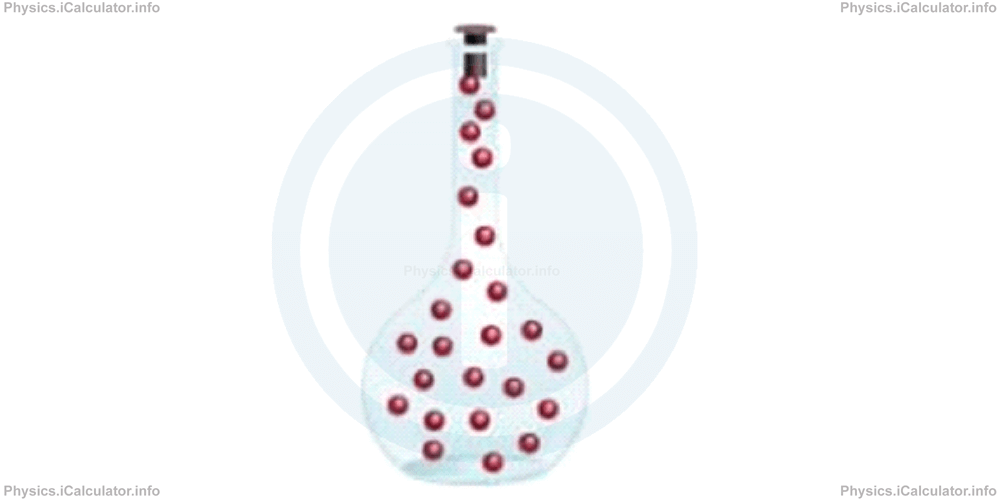
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 13.3.3 States of Matter. There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Absorption of Heat, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Absorption of Heat Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "States of Matter" physics lesson? People who liked the "Absorption of Heat lesson found the following resources useful:
- States Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this states (see below)
- Thermodynamics Physics tutorial: Absorption of Heat. Read the Absorption of Heat physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics Revision Notes: Absorption of Heat. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Absorption of Heat
- Thermodynamics Practice Questions: Absorption of Heat. Test and improve your knowledge of Absorption of Heat with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Thermodynamics questions with our excellent Thermodynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Thermodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning thermodynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Calorimetry (Heat Transfer)
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Absorption of Heat" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Thermodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Carnot Engine Efficiency Calculator
- Entropy Calculator
- Gas Laws Calculator
- Molecular Mean Free Path Calculator
- Translational Kinetic Energy Of Gas Calculator
- Root Mean Square Speed Calculator
- Ideal Gas Law Calculator
- Change In The Gas Internal Energy Calculator
- Radiative Heat Transfer Calculator
- Evaporative Heat Transfer Calculator
- Convective Heat Transfer Calculator
- Conductive Heat Transfer Calculator
- Final Temperature Of Mixture Calculator
- Heat Absorbed Or Released Calculator
- Thermal Expansion Calculator
- Temperature Calculator