Menu
Physics Lesson 18.1.3 - The Postulates
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on The Postulates, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
The Postulates
Regardless of the work done by Galileo Galilei and other scientists in the field of relativity, it is Einstein the person who is credited for putting the concept of relativity on scientific basis. Initially, Einstein formulated the Special Theory of Relativity, which is valid only for inertial frames of reference (in which the Newton's Laws of Motion can be applied, as explained earlier) and later, he generalized his findings by formulating the General Theory of Relativity, which is also valid for non-inertial frames that undergo gravitational acceleration (this is a complex theory which goes beyond the scope of this section).
Sometimes, findings and discoveries in science are difficult to be made in a straightforward way, through direct measurements and experiments. Therefore, indirect methods based on assumptions are often used in such cases to prove a certain theory. There are some basic concepts that are taken as true without proof and then, the new theory is built based on them. Such concepts are known as "postulates". In other words, a postulate is a thing suggested or assumed as true as the basis for reasoning, discussion, or belief.
Einstein based his Special Theory of Relativity upon two postulated:
- The laws of physics are the same and can be expressed in their simplest form in all inertial frames of reference (we discussed this point earlier in this tutorial). This is known as the relativity postulate. The laws of physics mentioned in this postulate include only those that satisfy this postulate.
- The speed of light in vacuum has the same value c in all directions and in all inertial reference frames. This is known as the speed of light postulate.
In other words, the second postulate implies that in universe, there is an ultimate speed c, which is the same in all directions and in all inertial frames of reference. Light is the only known thing that travels at this ultimate speed. No entity that carries energy or information can exceed this limit. Moreover, no particle that has mass can actually reach the ultimate speed c, no matter how much or for how long that particle is accelerated.
Precise measurements using modern devices have given the value c = 299,792,458 km/s for the speed of light in vacuum. We often round this value to 300,000,000 km/s or 3 Ă— 10-8 m/s. However, in this chapter (section) we will use the exact value to describe the speed of light in vacuum.
Both postulates have been tested many times but they have resulted always true. The existence of a limit to the speed of accelerated electrons was shown in an experiment carried out in 1964 by W. Bertozzi, who accelerated electrons to various measured speeds and through an independent method, he measured their kinetic energies. He found that as the force on a very fast electron is increased, the electron's measured kinetic energy increases toward very large values but its speed does not increase appreciably. The graph showing the relationship between the speeds of electrons and their kinetic energy is shown below.
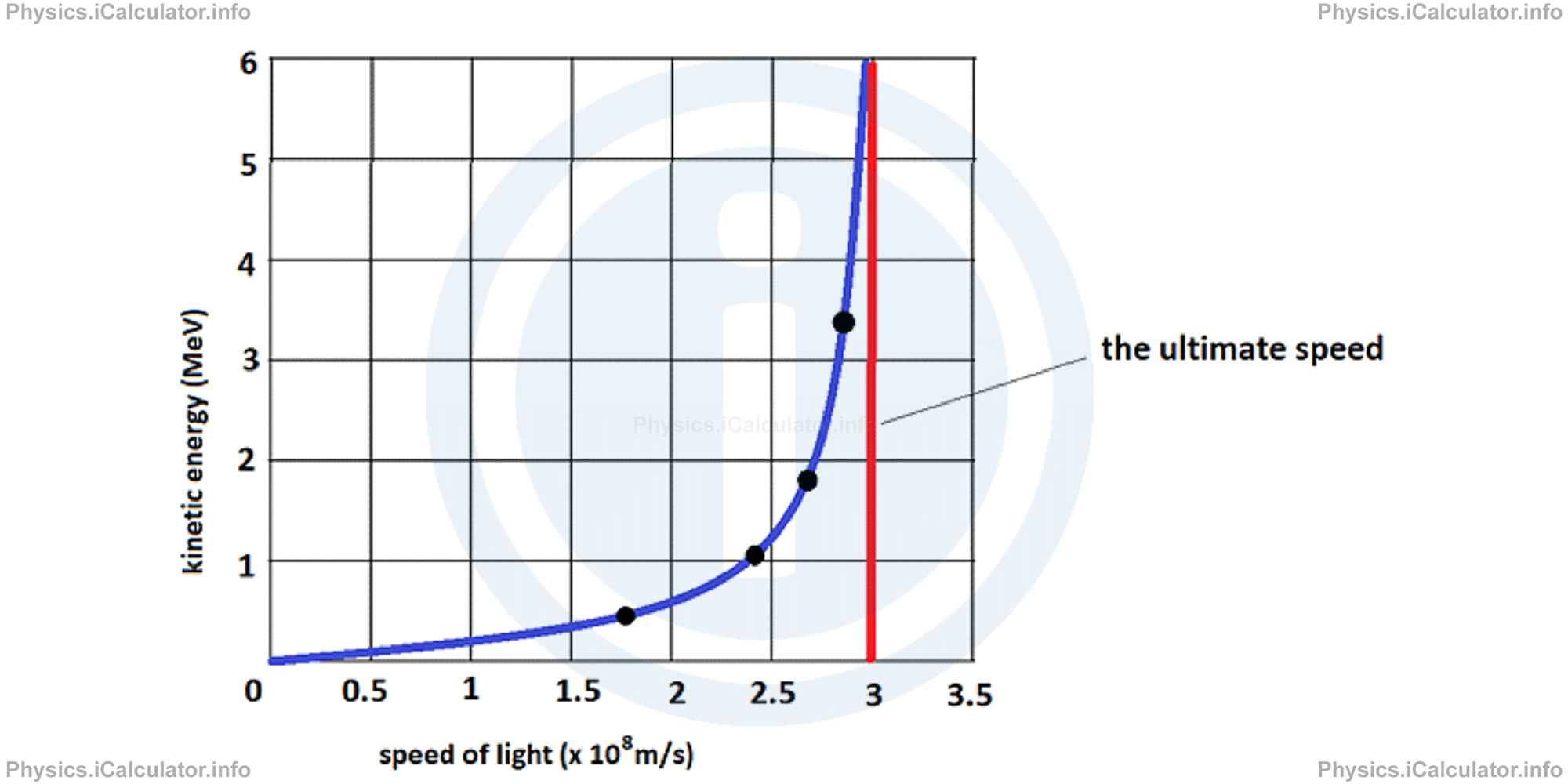
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 18.1.3 The Postulates. There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "The Postulates" physics lesson? People who liked the "Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws lesson found the following resources useful:
- Postulates Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this postulates (see below)
- Relativity Physics tutorial: Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws. Read the Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Relativity
- Relativity Revision Notes: Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws
- Relativity Practice Questions: Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws. Test and improve your knowledge of Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Relativity questions with our excellent Relativity calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Relativity Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning relativity - read our next physics tutorial: Classical Principle of Relativity
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Relativity. Galilean Transformations. Einstein's Postulates and Newton's Laws" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Relativity Calculators by iCalculator™
- Energy Calculator In Relativistic Events
- Frequency Calculator During Doppler Effect In Relativistic Events
- Length Calculator In Relativistic Events
- Lorentz Transformation Of Coordinates Calculator
- Lorentz Transformation Of Velocity Calculator
- Mass And Impulse Calculator In Relativistic Events
- Time Calculator In Relativistic Events
- Velocity Calculator In Relativistic Events