Menu
Physics Lesson 12.8.1 - Recap on Light Reflection
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Recap on Light Reflection, this is the first lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Recap on Light Reflection
In the previous Optics tutorials, we have explained that:
- Light propagates in straight lines despite being a wave. This is because there is no single wave travelling in space but a bundle of waves instead, called ray when very thin, or beam when the thickness is considerable or when light enlarges in space.
- Mirrors are reflecting surfaces used to change the direction of light.
- When light falls on a plane mirror, it is reflected back, i.e. it passes again in air when hitting the smooth surface of a plane mirror. This reflection is regular, i.e. we are able to see not only the amount (intensity) of the reflected light but also the image of objects around. This cannot occur when light hits a rough surface because it is reflected in a diffuse way, i.e. only the intensity of light is still the same but it is not possible to obtain any image of the surrounding objects.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal line lie all at the same plane (First law of Reflection).
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection (Second law of Reflection).
- Reflection of light occurs when a ray moving through the original medium (usually air) strikes a second medium (usually a smooth solid or liquid surface such as glass, still water etc.) and since it cannot penetrate through, it turns again to the original medium at the same pattern as shown in the figure below.
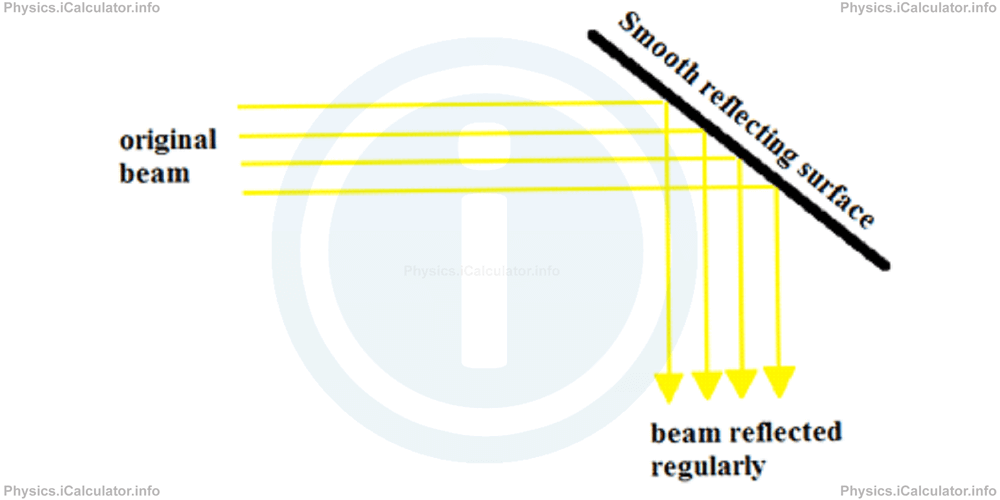
However, there are many other things to explain in this topic. First, it must be noted that the image formed in all plane mirrors has the same shape as the original object. Thus, a sphere will result in a spherical image in the mirror, a cylinder will give a cylindrical image, the reflection of a human body will result in the production of same kind of image on a mirror and so on. Therefore, if the shape of the original object is known, it is not necessary to use a very large number of rays to build the image after the reflection takes place but only a few rays emerging from the object's extremities. This saves us a lot of precious time during the study of objects' images on mirrors.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.8.1 Recap on Light Reflection. There are 8 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Recap on Light Reflection" physics lesson? People who liked the "Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors lesson found the following resources useful:
- Recap Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this recap (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors. Read the Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors
- Optics Practice Questions: Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors. Test and improve your knowledge of Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: Lenses. Equation of Lenses. Image Formation of Lenses
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.