Menu
Physics Lesson 12.8.4 - Image Formation in Concave Mirrors
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Image Formation in Concave Mirrors, this is the fourth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Image Formation in Concave Mirrors
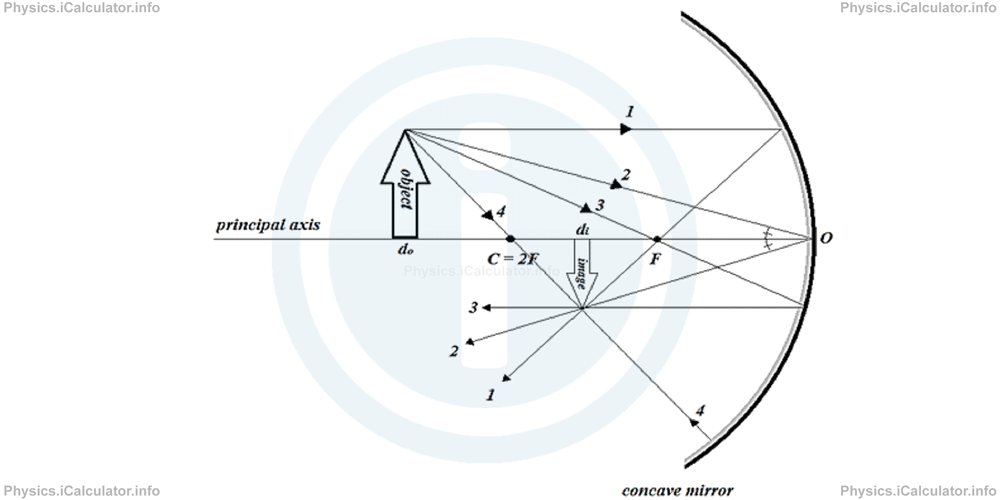
First, it is worth stating that all rays falling on a mirror whatever it may be (plane, concave or convex) are reflected at the same angle in respect to the normal line drawn from the mirror at the point in which the light is incident. Given this, we can identify four special rays among thousands of possible rays an object may produce. These special rays help us identify the position of image because the intersection of two of them gives us the position of the image's extremity.
More specifically, these four special rays are:
- The ray originating from the higher extremity of object and which is incident to the mirror in parallel to its axis of symmetry, otherwise known as principal axis. After touching the mirror, it is reflected through focus as shown earlier.
- The ray originating from the higher extremity of object, which touches the mirror at middle (at the origin of principal axis) and then is reflected at the same angle to the other side of symmetry axis.
- The ray originating from the higher extremity of object, which first passes through focus and then is reflected in parallel to the principal axis after touching the mirror (the inverse of ray 1).
- The ray originating from the higher extremity of object, which passes through the centre of curvature (twice the distance of focus). After touching the mirror it turns back because radius of sphere is normal to its inner surface at the point of the sphere in which it is incident.
The four rays discussed above are shown in the figure below.
Only two of the above special rays are enough to build up an image. There are six possible cases in image formation at concave mirrors based on the position of the object in respect to the mirror. They are:
- The object is beyond the centre of curvature (do > 2F). The special rays 1 and 4 are enough to build the image as shown in the figure.
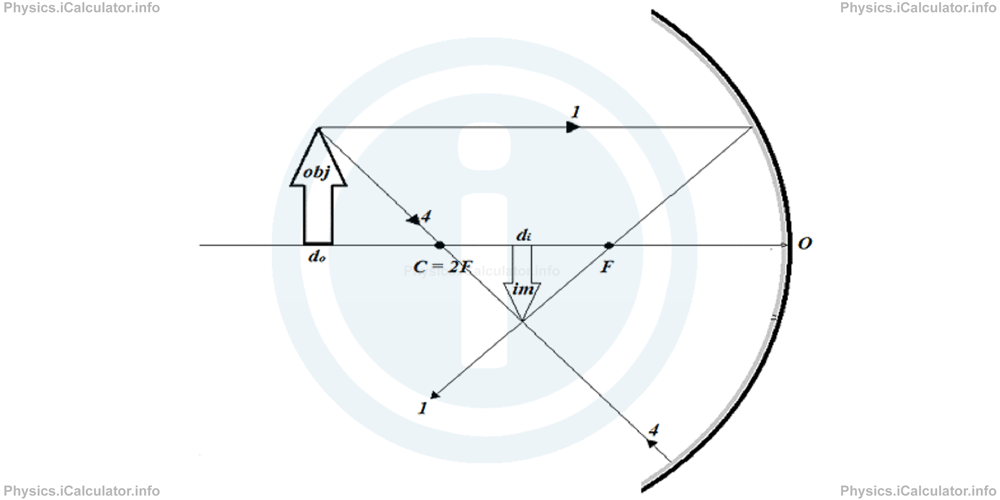 You can easily see that the image is diminished (smaller) and vertically inverted in respect to the object. This image is real as it is obtained by the reflected rays, not by their extensions, just like in plane mirrors.
You can easily see that the image is diminished (smaller) and vertically inverted in respect to the object. This image is real as it is obtained by the reflected rays, not by their extensions, just like in plane mirrors. - The object is at centre C of curvature, i.e. twice as far as the focus (do = 2F). We cannot use anymore the ray 4 but we can still use the other three special rays to build the image. Here let's use for example rays 1 and 3 for this purpose.
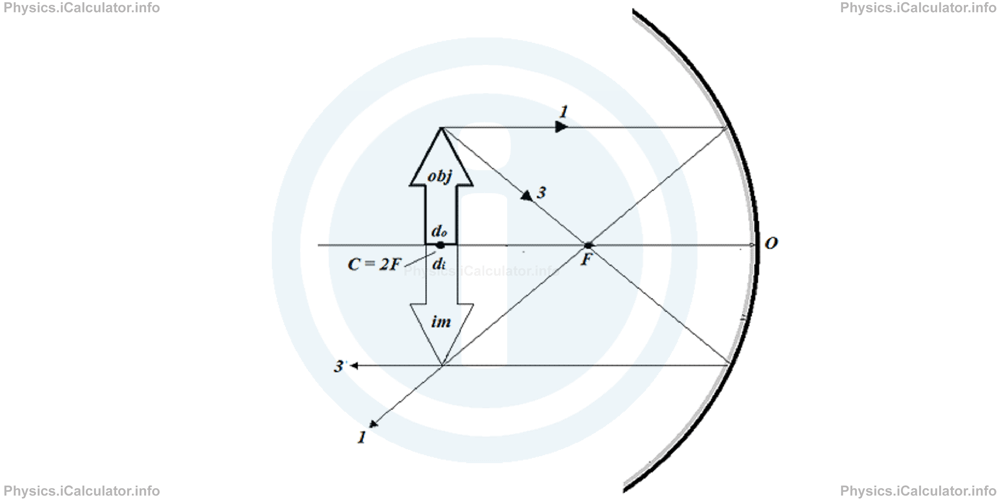 The image in this case is equal in size as the object but it is vertically inverted. It is formed at the same position (at centre of curvature) and is real because it is obtained by the reflected rays, not by their extensions.
The image in this case is equal in size as the object but it is vertically inverted. It is formed at the same position (at centre of curvature) and is real because it is obtained by the reflected rays, not by their extensions. - The object is located between the centre of curvature and focus (2F < do < F). We can use for example the rays 1 and 2 to build the image as shown below.
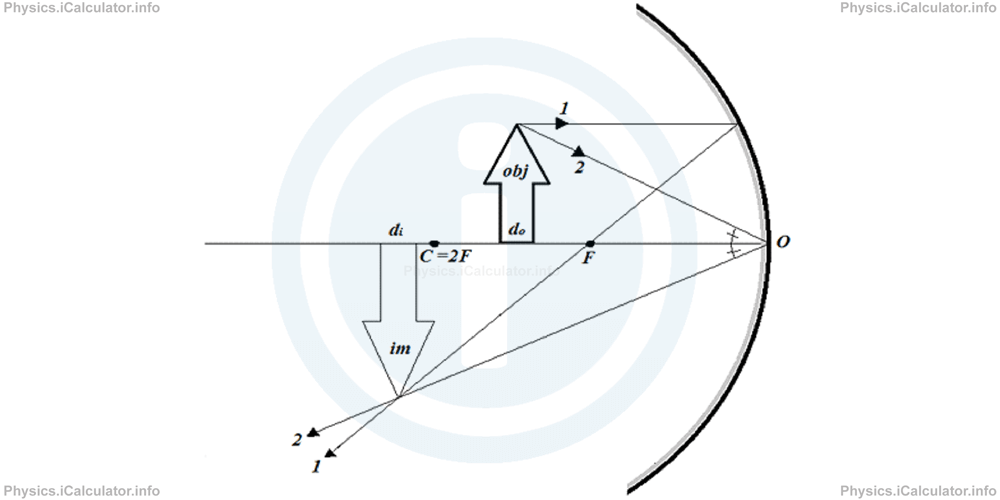 The image produced in this case is larger than the object. It is formed beyond the centre of curvature (dî > 2F) and it is real because it is formed by the reflected rays, not by their extensions.
The image produced in this case is larger than the object. It is formed beyond the centre of curvature (dî > 2F) and it is real because it is formed by the reflected rays, not by their extensions. - The object is located at focus of the concave mirror (do = F). In this case, the reflected rays are parallel to each other. This means no image is produced (in the language of mathematics we say 'the image is formed at infinity, as two parallel lines meet at infinity').
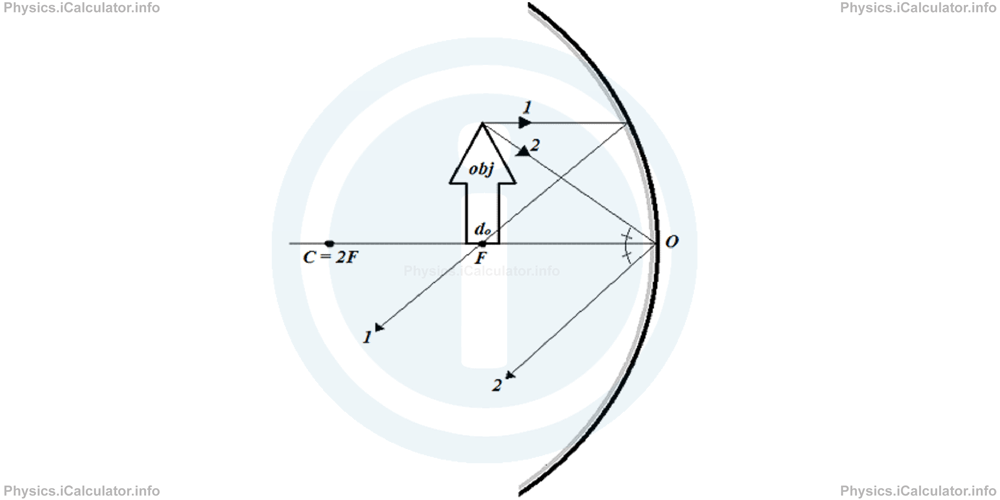
- The object is located closer to the concave mirror than focus (do < F). We can use again the special rays 1 and 2 to build up the image.
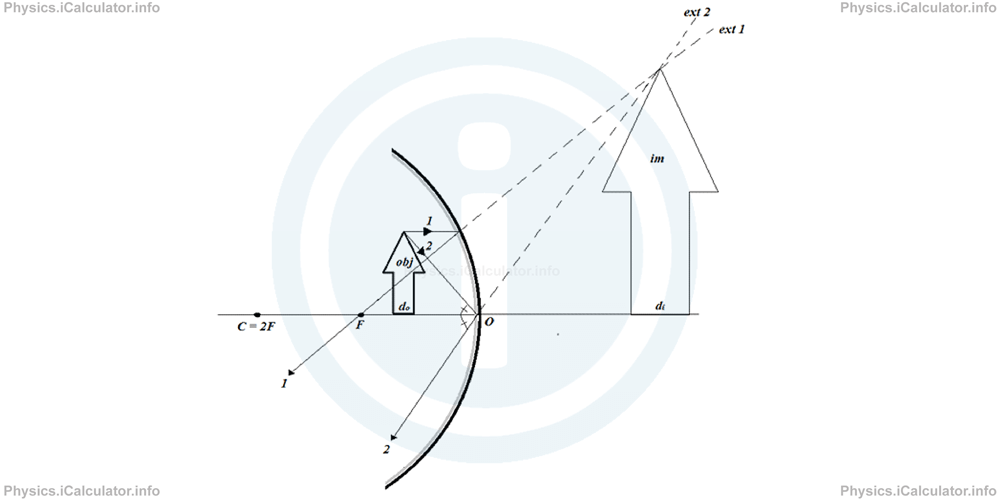 As you see, we cannot use the reflected rays to build up the image because they diverge from each other. Therefore, we use their extensions, which converge behind the mirror. As a result, an erect (upright) and larger image is formed at the position shown. Since this image is not obtained from the reflected rays but from their extensions, we say it is a virtual image.
As you see, we cannot use the reflected rays to build up the image because they diverge from each other. Therefore, we use their extensions, which converge behind the mirror. As a result, an erect (upright) and larger image is formed at the position shown. Since this image is not obtained from the reflected rays but from their extensions, we say it is a virtual image. - The object is at infinity. In this case, only a parallel bundle of rays comes from the object to the mirror. As a result, the image will be simply a bright dimensionless point at focus, just like when we direct the mirror towards the sunlight.
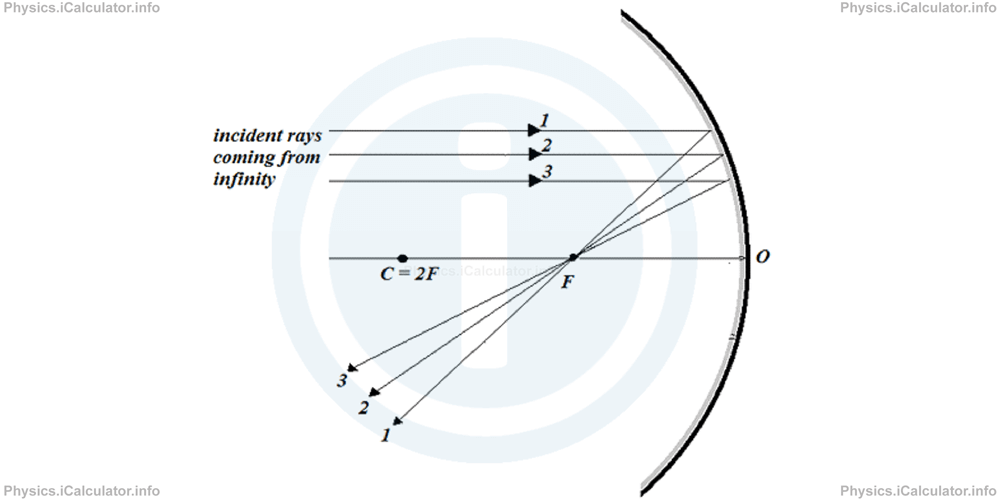
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 12.8.4 Image Formation in Concave Mirrors. There are 8 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Image Formation in Concave Mirrors" physics lesson? People who liked the "Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors lesson found the following resources useful:
- Concave Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this concave (see below)
- Optics Physics tutorial: Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors. Read the Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Optics
- Optics Revision Notes: Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors
- Optics Practice Questions: Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors. Test and improve your knowledge of Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Optics questions with our excellent Optics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Optics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning optics - read our next physics tutorial: Lenses. Equation of Lenses. Image Formation of Lenses
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Mirrors. Equation of Curved Mirrors. Image Formation in Plane and Curved Mirrors" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.