Menu
Physics Lesson 20.1.3 - Experiment of Rutherford
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Experiment of Rutherford, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Experiment of Rutherford
Rutherford carried out an experiment for determining the scattering angle of alpha particles (now we know that alpha particles are Helium nuclei but the concept of atomic nuclei was still unknown at that time) when they penetrate a thin golden foil. After emitted from the source, alpha particles were allowed to pass through a very thin hole in order to obtain a regular one-dimensional beam.
After passing through the thin golden foil, most alpha particles continued their motion undisturbed in the original direction. However, a few of them deflected and hit a screen placed at right angle to the golden foil, as shown in the figure.
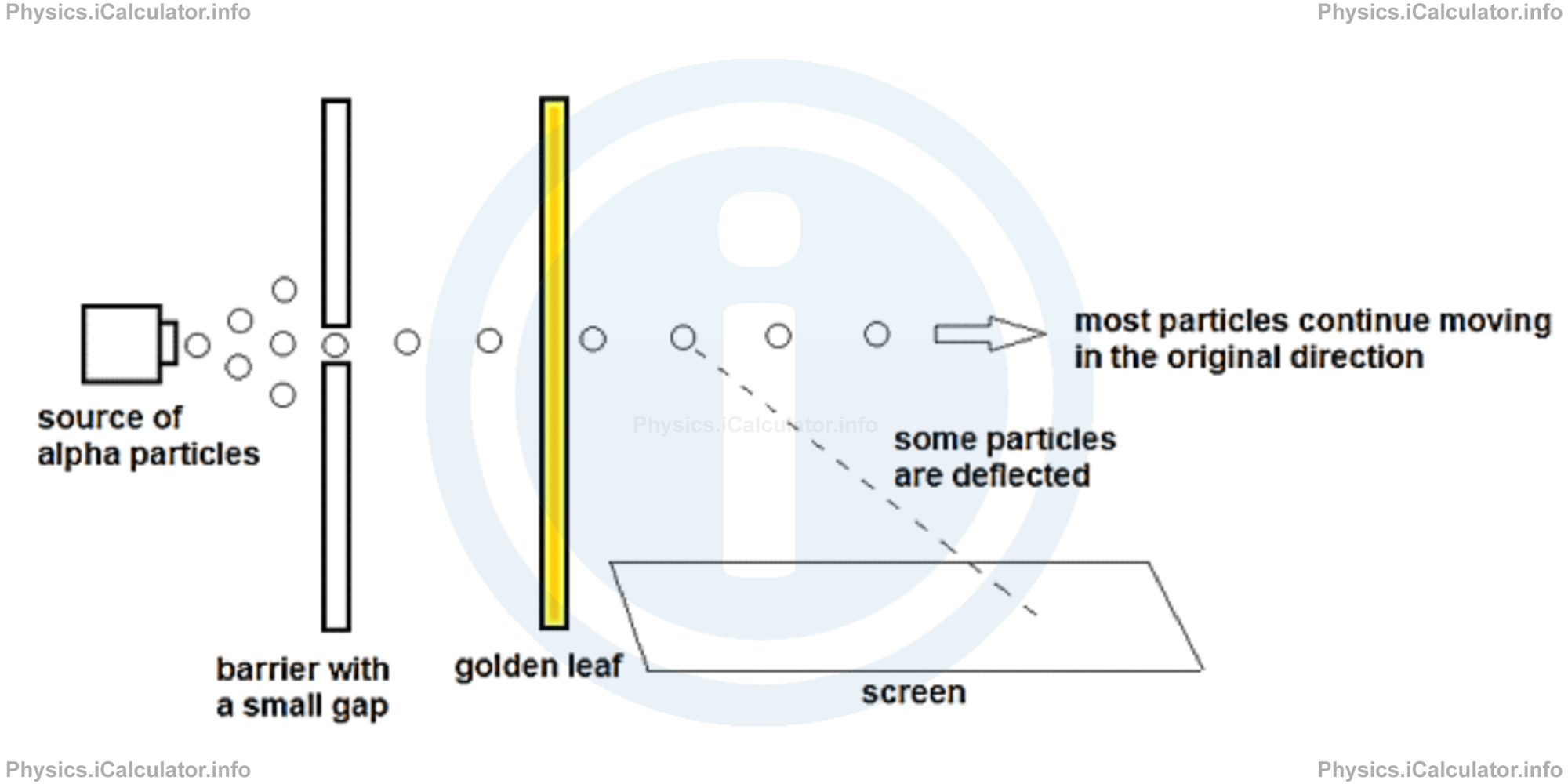
The screen was made by zinc sulfide, a material that produces bright spots when hit by alpha particles. The figure shows only one screen but Rutherford placed two parallel screens in both sides of the golden foil in order to convince himself that the phenomenon of bright spots was not casual.
If Thompson model were correct, alpha particles would not deflect as according this model there are many spaces with positive charge inside the atom. Even if any alpha particle encounters an electron during its motion inside the gold atoms, the resulting electric force would be very small to make it deflect so much, i.e. the deflection caused by electric force between alpha particles and electrons is quite unnoticeable (less than one degree).
However, Rutherford noticed that some particles were deflected at a large angle, some even turned back. He was very surprised by this phenomenon. Later, in an interview he declared: "This was incredible - it is like firing a 15-inch artillery shell at a sheet of tissue paper and the shell came back to hit you."
The only reasonable explanation of this strange phenomenon was that the positive charge is not distributed evenly throughout the atom but it is rather concentrated at the centre of atom, where it causes a large repelling force on other positive charges coming towards them (such as the case of alpha particles). Hence, it was clear that the Thompson model of atom is not true and another atomic model that takes into consideration the new discoveries was necessary to introduce.
Rutherford's Atomic Model
In the light of new discoveries, Ernest Rutherford therefore proposed his new version of atomic model. According to this model, an atom consists on a small positively charged nucleus at its centre, where most of atomic mass is concentrated. As for electrons, they revolve around the nucleus to preserve the atom's electric neutrality. Look at the figure:
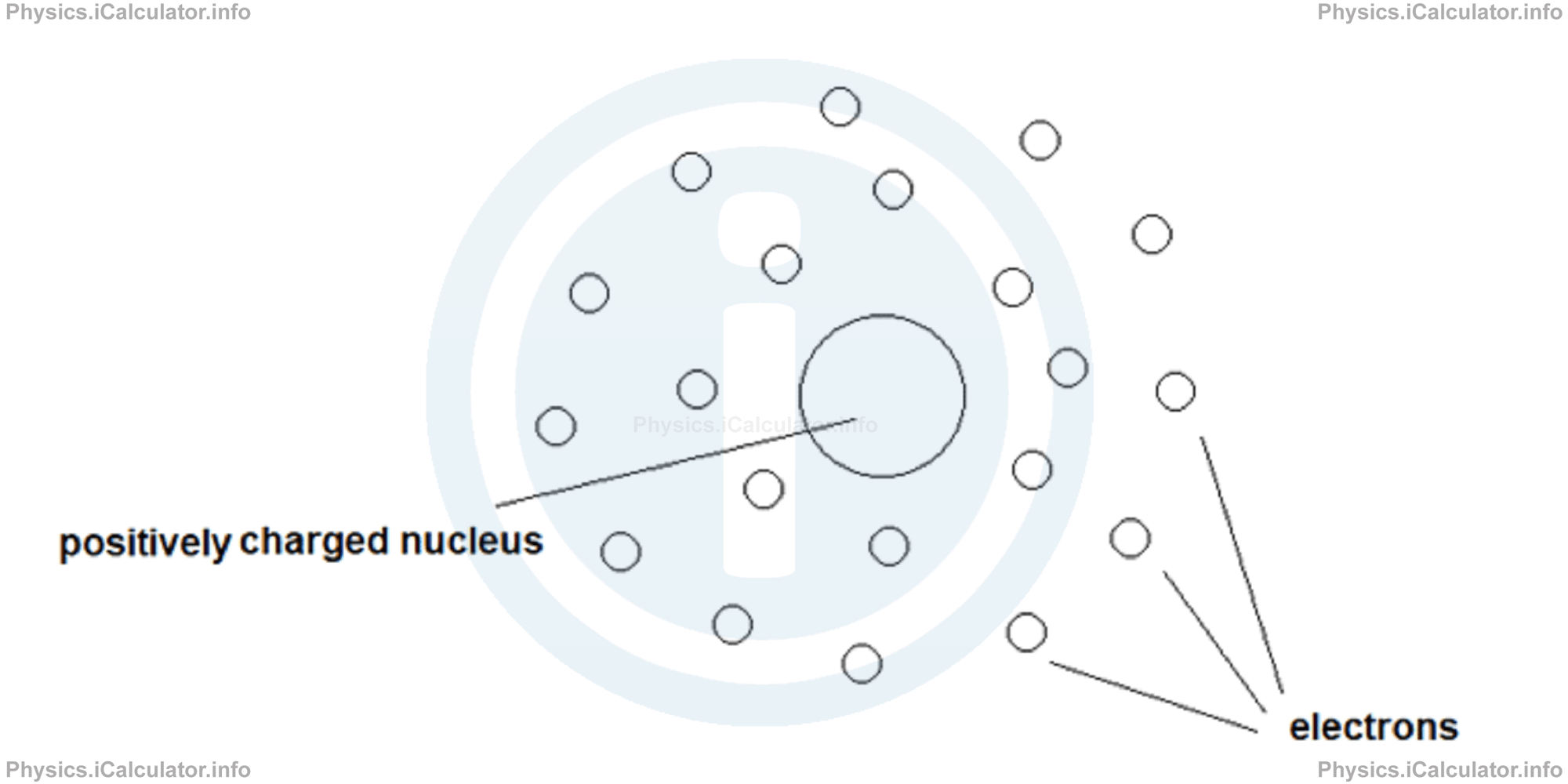
This model provides a satisfactory explanation to the phenomenon of alpha particles deflection after penetrating the golden foil. However, in Rutherford's model there is a serious shortcoming. It could not explain the stability of atom in the sense that when electrons revolve around the nucleus, they lose energy and eventually collide with the nucleus.
Hence, despite Rutherford's atomic model was a further step towards the truth, it was incomplete and therefore, it required revision. Niels Bohr made a further advancement in this direction with the new atomic model he proposed.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 20.1.3 Experiment of Rutherford. There are 9 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Experiment of Rutherford" physics lesson? People who liked the "Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties lesson found the following resources useful:
- Rutherford Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this rutherford (see below)
- Nuclear Physics Physics tutorial: Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties. Read the Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Nuclear Physics
- Nuclear Physics Revision Notes: Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties
- Nuclear Physics Practice Questions: Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties. Test and improve your knowledge of Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Nuclear Physics questions with our excellent Nuclear Physics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Nuclear Physics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning nuclear physics - read our next physics tutorial: Nuclear Forces, Defect of Mass and Binding Energy
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Atomic Nucleus and Its Structural Properties" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.