Menu
Physics Lesson 3.2.2 - What is Position? How does it differ from Location?
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on What is Position? How does it differ from Location?, this is the second lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Position, Reference Point, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
What is Position? How does it differ from Location?
We can show the location of an object by a finger, or by drawing a small dot in the place where the object lies. If the object is voluminous, we usually put a small dot at the object's centre to show its location as in the figure below.
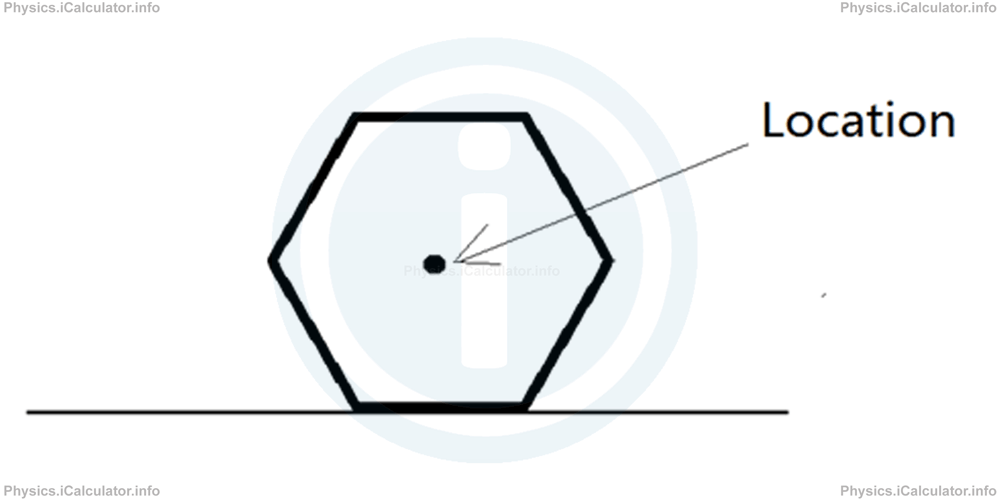
It is obvious that location does not imply the use of any reference point or coordinate. Therefore, no numerical values are involved when dealing with the location of an object.
On the other hand, Position is a physical quantity that shows how far an object from the origin (reference point) is. Position not only has a magnitude (numerical value) but it also has a direction. It is not the same thing if we say, "the object is 6m on the left of the reference point" and "the object is 6m on the right of the reference point" although the distance from the origin (reference point) is the same in both cases (6 m).
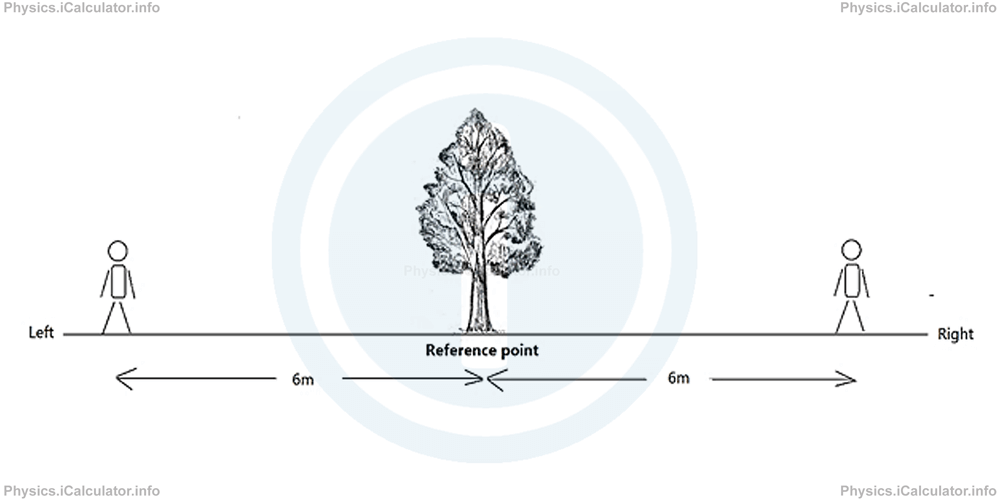
Thus, there are two men in the figure; each of them is at 6m from the tree, which in this case acts as a reference point or origin. Therefore, it is obvious it is not enough knowing only the distance from the reference point but we must know the direction as well. Only then, we can exactly determine the position of a given object.
As we discussed in Physics Tutorial 2.1 "Vectors and Scalars in Physics", a quantity for which direction information is required is known as "vector quantity." This is the case for the position of an object.
By definition, "Position is a vector quantity that shows how far an object is from the origin in a given direction."
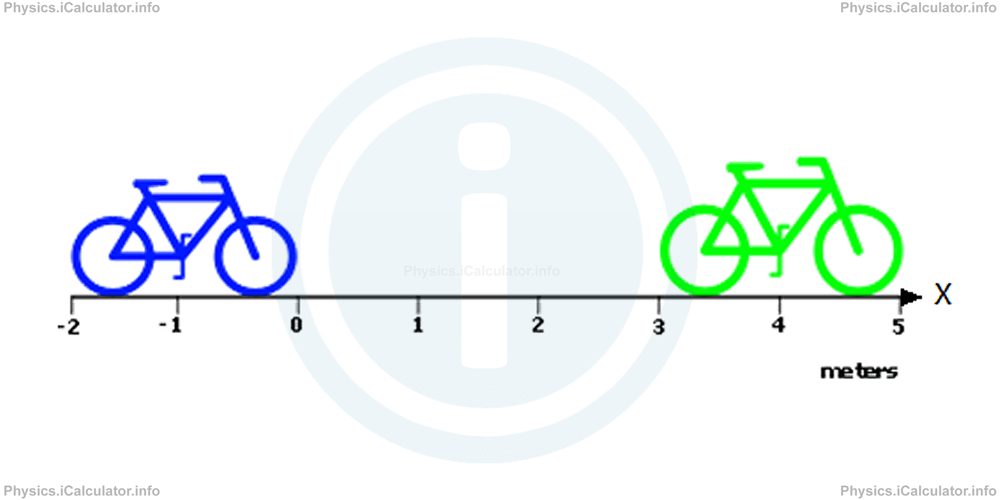
Position can be positive, negative or zero. It can be positive when the location of the object is at the positive part of the position axis. For example, the position of the green bicycle shown below is positive as its location is at (+4) m. As for the position of the blue bicycle, it is negative because its location is at (-1) m. (Remember, for voluminous and irregularly shaped objects we consider the actual location at the centre of the object). Position can be zero when the object is located at the reference point.
You have reach the end of Physics lesson 3.2.2 What is Position? How does it differ from Location?. There are 3 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Position, Reference Point, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Position, Reference Point Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "What is Position? How does it differ from Location?" physics lesson? People who liked the "Position, Reference Point lesson found the following resources useful:
- Location Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this location (see below)
- Kinematics Physics tutorial: Position, Reference Point. Read the Position, Reference Point physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Kinematics
- Kinematics Revision Notes: Position, Reference Point. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Position, Reference Point
- Kinematics Practice Questions: Position, Reference Point. Test and improve your knowledge of Position, Reference Point with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Kinematics questions with our excellent Kinematics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Kinematics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning kinematics - read our next physics tutorial: Displacement and Distance in 1 Dimension
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Position, Reference Point" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.