Menu
Physics Lesson 14.3.1 - What Is Electric Field? Similarities between Gravitational and Electric Field
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on What Is Electric Field? Similarities between Gravitational and Electric Field, this is the first lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Field, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
What Is Electric Field? Similarities between Gravitational and Electric Field
In the tutorial "Electric Charges. Conductors and Insulators", we have seen that one of methods used for building up charges in objects is induction. In this method, a charged object is brought near a neutral one. As a result, the neutral object is locally charged with opposite signs despite the total amount of extra charge in this object is zero.
This phenomenon is the best indicator that electric charges are generated not only when the objects are in contact, but also when there is a certain distance between them.
Since such an interaction is quantitatively represented through the concept of electrostatic force, we can conclude that electrostatic force is a force that acts in distance, like the gravitational force we have discussed earlier. Yet, there is a similarity in the formulae of these two forces as well. Look at the table below.
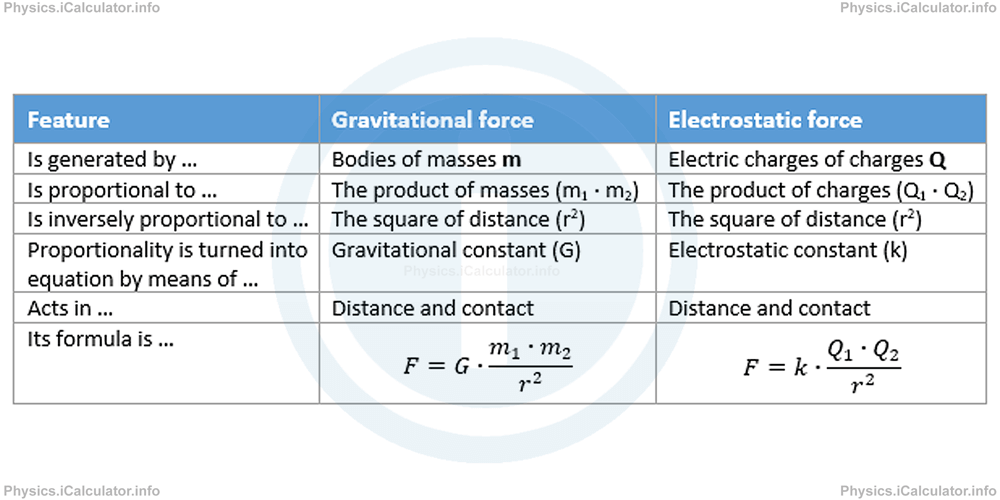
Given the above analogies, we can elaborate further this approach, i.e. analyse the similarities between gravity and electrostatics. Thus, given that gravitational force is produced from the gravitational field generated by the massive objects (which is the space around an object in which its gravitational attraction is present), we can deduce that there must exist an electrostatic field as well, i.e. a space around a charged object in which the attractive or repulsive effect of charged objects is observed.
Let's elaborate further this new concept by using again the analogy between gravity and electrostatics.
We have seen that gravitational field is represented mathematically by means of gravitational field strength g. The simplified formula for gravitational force of an object on Earth surface is
Therefore, the gravitational field strength of Earth acting on the object of mass m is
In the same way in which we calculate the magnitude of gravitational field strength g (i.e. by finding the weight of a 1 kg object at rest on the Earth surface, which corresponds to the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on that object), we can also calculate the magnitude of electrostatic field E. This can be achieved by considering a +1C test charge Q0 brought near a charged object and then measuring the electrostatic force exerted by this charged object to the test charge. Thus, we can write
Since the formula of electrostatic force exerted by a charge Q on the test charge Q0 is
we can find the corresponding (long) formula for the electrostatic field generated by the charge Q and experienced by the test charge Q0 which is at distance r from the charge Q:
= k × Q × Q0/r2/Q0
= k × Q/r2
The unit of electrostatic field (for now) is [N/C]. (We will see in the next tutorial that there is another unit that is officially recognized as the unit of electrostatic field in the SI system of units).
In this way, we obtain the definition of electrostatic (or electric) field, that is
Electric field is the amount of electrostatic force exerted by a charged object on a test charge, which is at a certain distance from object.
Remark!
Despite many similarities between electric and gravitational fields, there is one important difference between them. Gravitational field has only attractive nature while electric field may have attractive or repulsive nature, in dependence of the charges involved.
Example 1
What is the electrostatic field produced by a + 8 μC point charge at 2 m away from it? Take k = 9 × 109 N × m2 / C2.
Solution 1
Clues:
Q = + 8 μC = + 8 × 10-6 C
r = 2 m
k = 9 × 109 N × m2 / C2
We have:
= 9 × 109 × 8 × 10-6/22
= 18 × 103 N/C
= 18 000 N/C
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 14.3.1 What Is Electric Field? Similarities between Gravitational and Electric Field. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Field, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Field Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "What Is Electric Field? Similarities between Gravitational and Electric Field" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Field lesson found the following resources useful:
- Definition Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this definition (see below)
- Electrostatics Physics tutorial: Electric Field. Read the Electric Field physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrostatics
- Electrostatics Revision Notes: Electric Field. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Field
- Electrostatics Practice Questions: Electric Field. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Field with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrostatics questions with our excellent Electrostatics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrostatics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrostatics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Potential Energy
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Field" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.