Menu
Physics Lesson 14.3.6 - Conductors in an Electric Field
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Conductors in an Electric Field, this is the sixth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Field, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Conductors in an Electric Field
As explained in previous tutorials, conductors are materials that allow electricity flowing through them. Furthermore, their atoms have free electrons available, which can carry electricity in other parts.
Now, let's see what happens if we place a metal slab inside a uniform electric field. The free electrons of metal experience an electric force which is in the opposite direction of the electric field, because electric field lines extend from positive to negative charges and since electrons are negative, they tend to go in the opposite direction to the field lines as they are attracted by the positive charges which have produced the electric field.
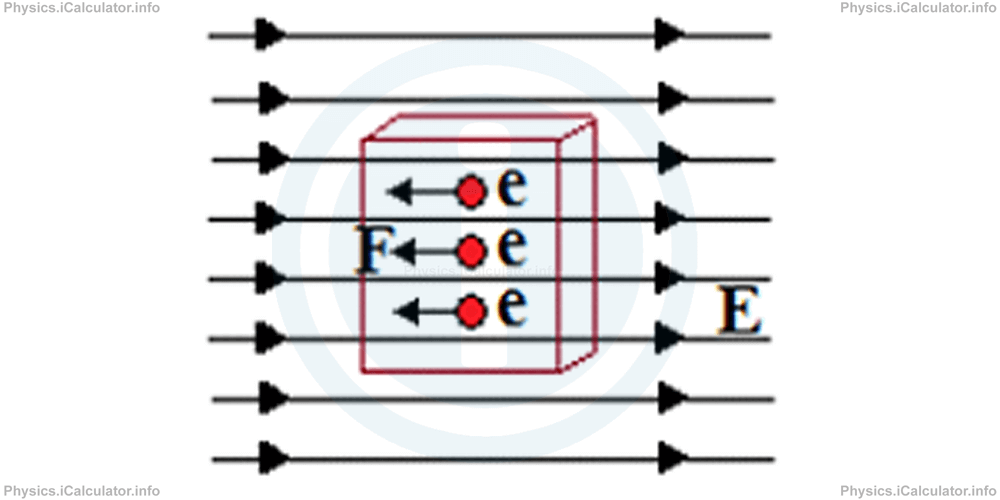
As a result, the electrons accumulate on the left part of the slab, leaving the right part positively charged. Hence, an electric field E' is generated inside the slab, whose direction is opposite to the electric field outside.
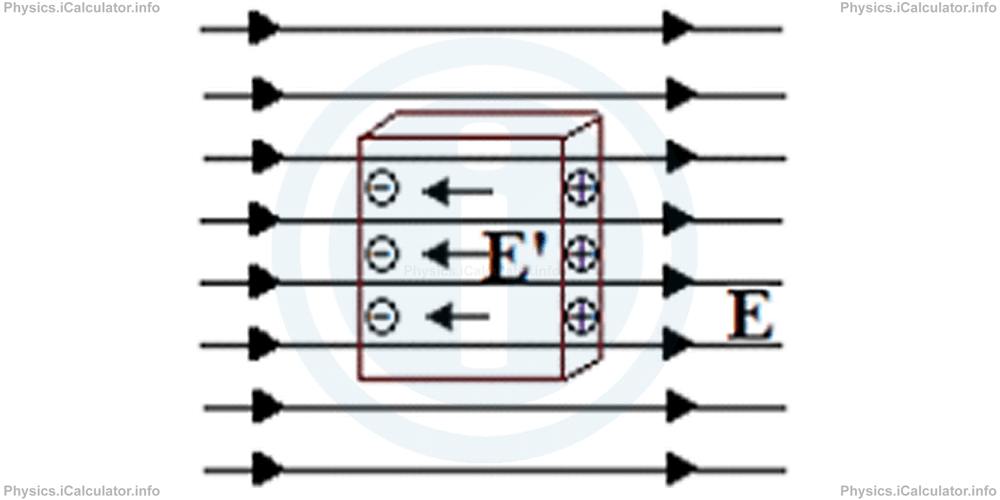
The charge accumulation continues until the magnitude of the electric field inside the slab becomes equal to that outside the slab, i.e. until |E| = |E'|. From this moment and on, the resultant electric field inside the slab becomes zero.
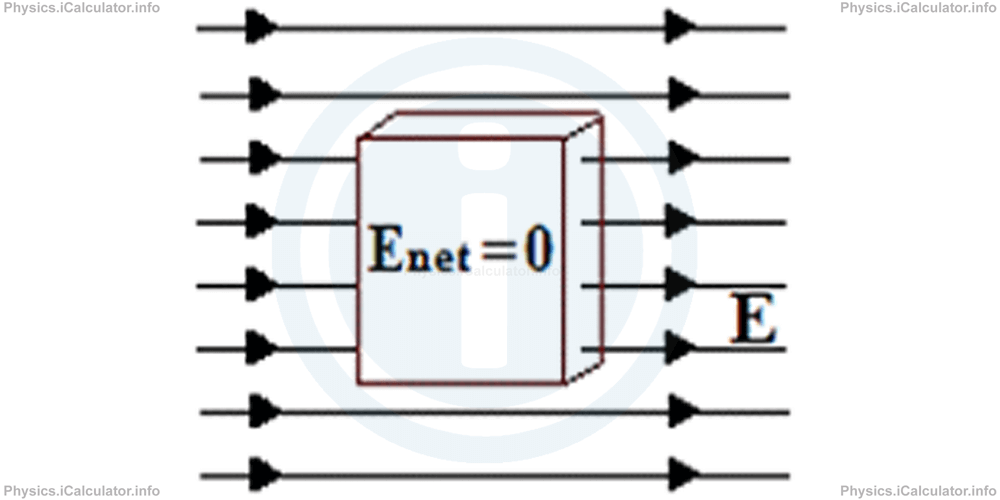
In few words, the electric field inside a conductor is zero. This means when we place a charge inside a cavity of a conductor, the charge does not move, as it does not experience any electric force.
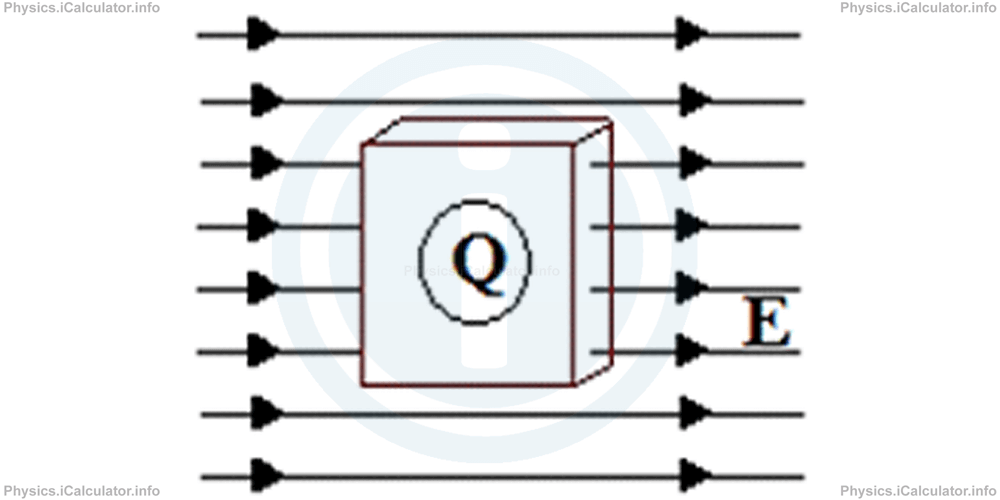
This property has a wide range of applications in physics. It had been discovered by Faraday, who invented the famous Faraday's Cage, a conducting spherical grid whose internal space has zero electric field despite the grid is charged. Many electric-related phenomena have been studied by inserting the apparatuses inside such a cage, as in this way they are not affected by the surrounding electric field.
Example 4
A hollow metal box is placed inside a magnetic field produced by two plates as shown in the figure.
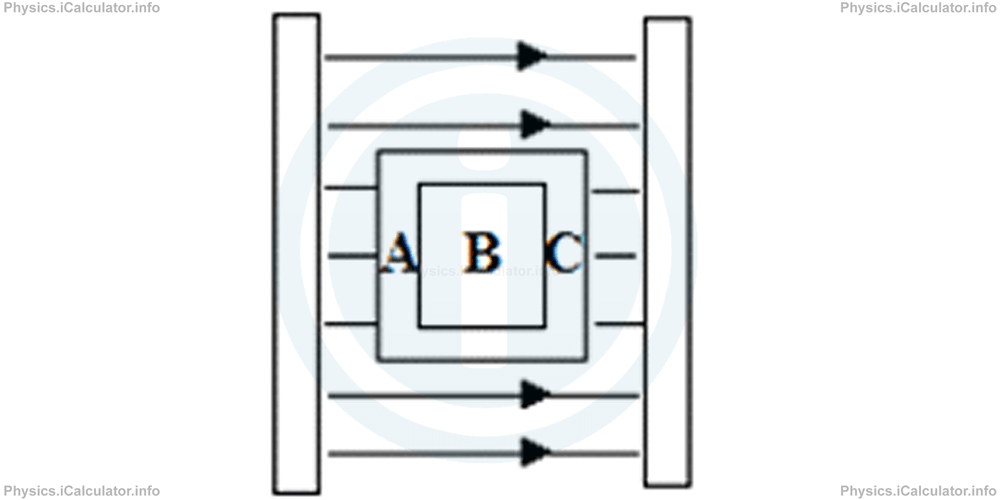
What is the direction of electric field in the sections A, B and C of the figure?
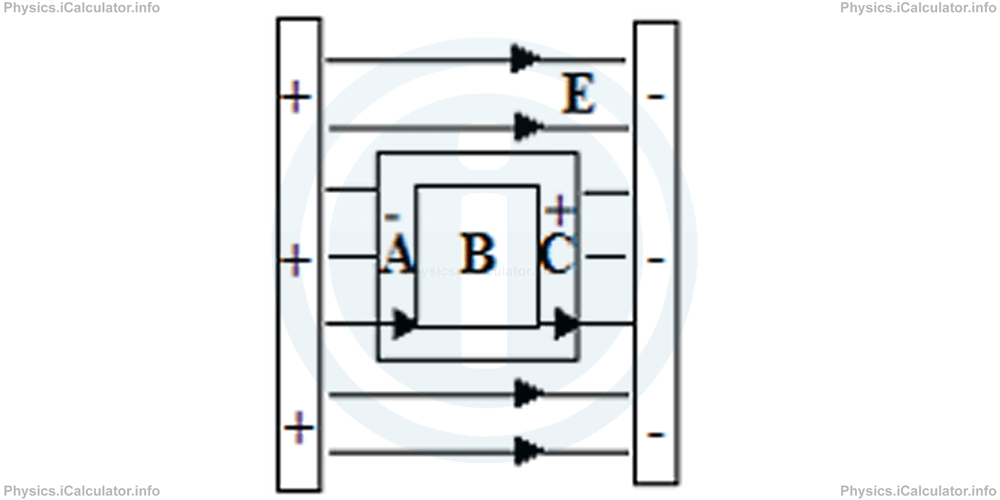
Solution 4
It is known that electric field lines extend from positive to negative. This means, the left plate is positively charged while the right one is negatively charged. Thus, the part A of the box contains extra negative charges while the part C contain extra positive ones (opposite charged attract each other). When the equilibrium is reached, the opposite electric field produced inside the box cancels the field E and as a result, there is no electric field at the section B.
On the other hand, sections A and C are exposed to the external field. As a result, in both sections the direction of electric field is from left to right, just like the original field.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 14.3.6 Conductors in an Electric Field. There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Field, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Field Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Conductors in an Electric Field" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Field lesson found the following resources useful:
- Conductors Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this conductors (see below)
- Electrostatics Physics tutorial: Electric Field. Read the Electric Field physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrostatics
- Electrostatics Revision Notes: Electric Field. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Field
- Electrostatics Practice Questions: Electric Field. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Field with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrostatics questions with our excellent Electrostatics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrostatics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrostatics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Potential Energy
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Field" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.