Menu
Physics Lesson 15.3.4 - Ohm's Law for the Whole Circuit
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Ohm's Law for the Whole Circuit, this is the fourth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Ohm's Law for the Whole Circuit
The battery has its own internal resistance, which we denote as r. We can draw this conclusion when we touch a battery immediately after it has been operating. We can feel the hotness of battery, which indicates the conversion of electricity into heat inside the battery.
In addition, from the previous tutorial, we know that a conductor has its own internal resistance, which depends from the type of material, length and thickness of conductor. This causes a drop in the potential difference at the resistor. Look at the figure below.
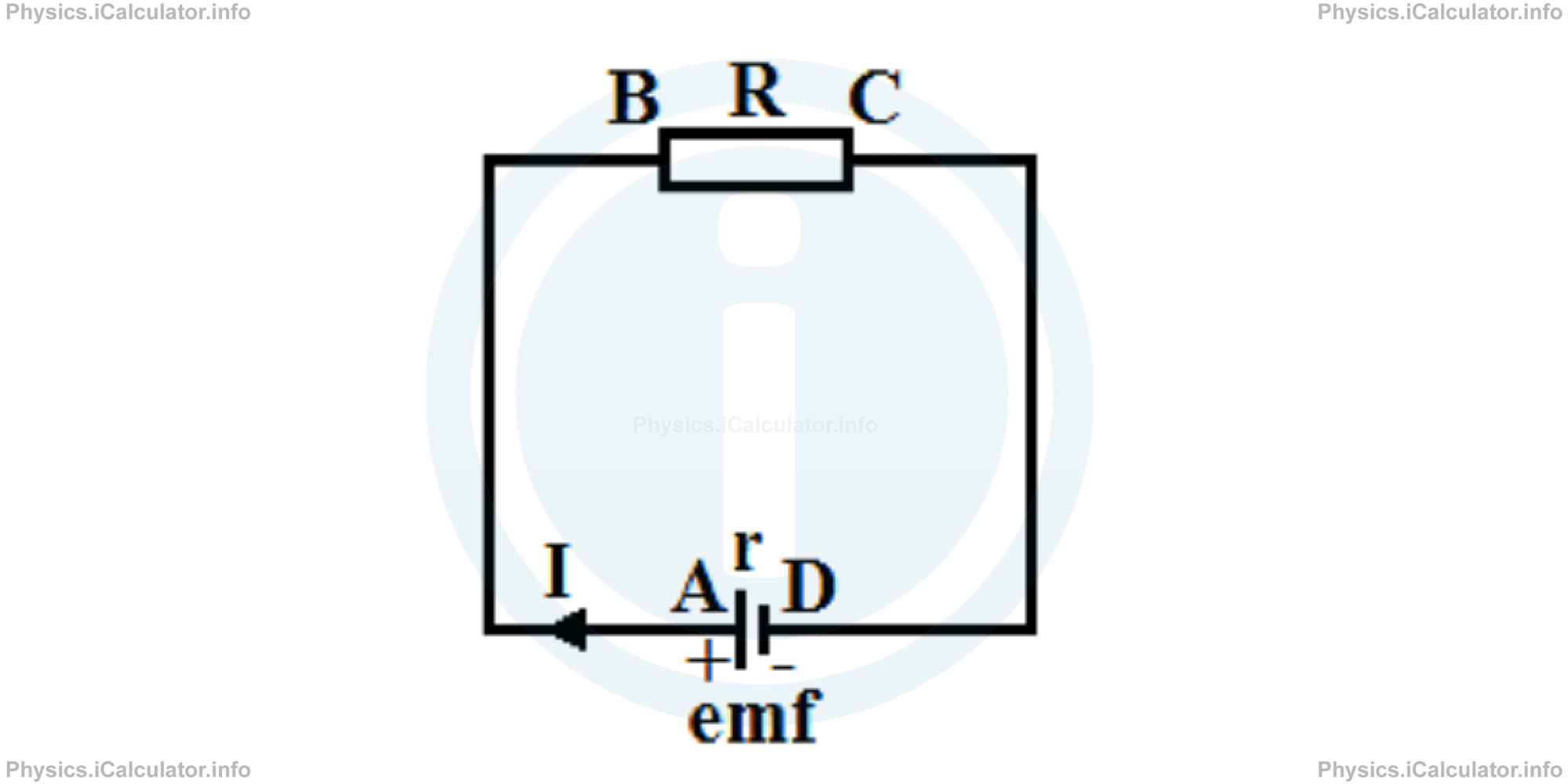
We can write for the relationship between potential differences and the electromotive force in the above circuit:
If we write the total resistance of the circuit by Rtot, we obtain (applying Ohm's Law):
Given that RABCD = Rwire, we obtain
or
The above equation gives Ohm's Law for the whole circuit. We can write it in a shorter way as
Example 4
A 20 m long copper wire of 4 mm2 thickness (ρ = 1.69 × 10-8 Ω ∙ m) is used to build an electrical circuit that contains a 24 V battery and a resistor. The battery has a 0.6 Ω internal resistance. What is the resistance of the resistor if the current flowing through the circuit is equal to 12A? Use the figure shown in the theory as a reference.
Solution 4
Clues:
L = 20 m
A = 4 mm2 = 4 × 10-6 m2
emf = 24 V
r = 0.6 Ω
I = 12 A
R = ?
First, we find the resistance of wire. We have
= (1.69 × 10-8 Ω ∙ m) ∙ (20m)/4 × 10-6 m2 )
= 8.45 × 10-2 Ω
= 0.0845 Ω
Applying Ohm's Law for the whole circuit, we obtain
r + R + Rw = Rtot = emf/I
= 24 V/12 A
= 2 Ω
Thus,
= 2 Ω - 0.6 Ω - 0.0845 Ω
= 1.3155 Ω
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 15.3.4 Ohm's Law for the Whole Circuit. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Ohm's Law for the Whole Circuit" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law lesson found the following resources useful:
- Whole Circuit Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this whole circuit (see below)
- Electrodynamics Physics tutorial: Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law. Read the Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrodynamics
- Electrodynamics Revision Notes: Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law
- Electrodynamics Practice Questions: Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrodynamics questions with our excellent Electrodynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrodynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Circuits. Series and Parallel Circuits. Short Circuits
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Potential Difference (Voltage). Ohm's Law" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Electrodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Amount Of Substance Obtained Through Electrolysis Calculator
- Charge Density Calculator
- Electric Charge Stored In A Rc Circuit Calculator
- Electric Field In Terms Of Gauss Law Calculator
- Electric Power And Efficiency Calculator
- Electron Drift Velocity Calculator
- Equivalent Resistance Calculator
- Force Produced By An Electric Source Calculator
- Joules Law Calculator
- Ohms Law Calculator
- Potential Difference In Rc Circuit Calculator
- Resistance Due To Temperature Calculator
- Resistance Of A Conducting Wire Calculator