Menu
Physics Lesson 4.2.2 - What are the factors affecting the Gravitational Force?
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on What are the factors affecting the Gravitational Force?, this is the second lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
What are the factors affecting the Gravitational Force?
From our experience, we know (as stated before) that Earth attracts us. Thus, when we jump, we fall again on the ground due to this attraction. However, it is a fact that we attract the Earth as well, although the effect caused by the Earth attraction in our body is more noticeable than the attraction effect caused by our body on the Earth, due to the difference in size between the Earth and us. Therefore, the effect of gravitational attraction is mutual.
The fact that the gravitational attraction of Earth is more noticeable than that of any other object near its surface, makes us think (rightfully) that the gravitational force depends on the mass of the objects involved. Thus, more massive the object, greater the gravitational field (and therefore, the resulting gravitational force) produced. This means gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of masses of the objects involved.
Another factor affecting the magnitude of Gravitational Force between two objects is the distance between them. It is obvious that the farther away the objects be, weaker the resulting gravitational force produced is. This means the Gravitational Force is inversely proportional to the product of the distance between the two objects.
Mathematically, we can write:
Equation 1a
Fg = G × m1 × m2/R2where m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects involved, and R is the distance between the objects (from centre to centre, not from surface to surface).
The quantity G is a constant. It is known as the gravitational constant. Its numerical value is
The value of constant G has been calculated experimentally.
Look at the figure below:
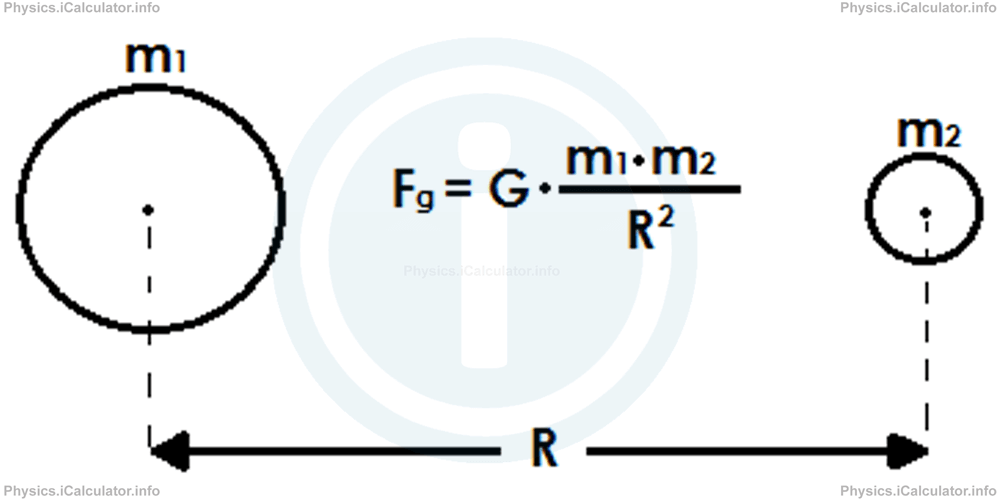
If one object is much heavier than the other, we write M and m for their masses instead of m1 and m2, where M stands for the heaviest object and m for the lightest one.
Example 1
What is the gravitational force exerted by the Earth at a 1 kg object resting on its surface? Take the mass of the Earth equal to 5.972 × 1024 kg and the Radius of the Earth equal to 6371 km.
Solution 1
Clues:
m = 1 kg
R = 6371 km = 6 371 000 m = 6.371 × 106 m
G = 6.674 × 10-11 N × m2/kg2
Thus, since
Equation 1b
Fg = G × M × m/R2we obtain after substituting the known values,
= 39.86 × 1013/40.59 × 1012
= 0.981 × 101 N
= 9.81N
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 4.2.2 What are the factors affecting the Gravitational Force?. There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "What are the factors affecting the Gravitational Force?" physics lesson? People who liked the "Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight lesson found the following resources useful:
- Factors Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this factors (see below)
- Dynamics Physics tutorial: Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight. Read the Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Dynamics
- Dynamics Revision Notes: Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight
- Dynamics Practice Questions: Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight. Test and improve your knowledge of Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Dynamics questions with our excellent Dynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Dynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning dynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Types of Forces II. Resistive Forces (Frictional Force. Drag). Terminal Velocity
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Types of Forces I. Gravitational Force and Weight" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.