Menu
Physics Lesson 4.4.4 - What is Tension?
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on What is Tension?, this is the fourth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension), you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
What is Tension?
Tension is another resistive force that appears when a string is pulling a load. In other words, tension is the resistive force of a string against deformation caused when it is pulling an object. It is obvious that tension is in the opposite direction of the pulling force as shown in the figures below.
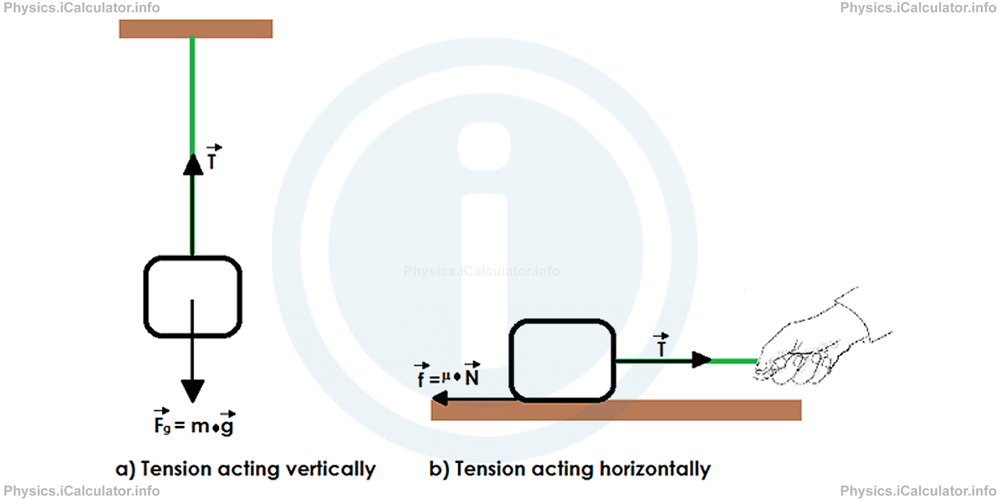
In the first case (figure a) the tension acts against the gravity, while in the second case (figure b), it acts against friction. Tension has an intermolecular nature, i.e. it appears when the molecules of the string (which is a solid and as such, its molecules have a strong connection between them) display resistance towards extension.
Tension is different from elastic force, as it appears when the string is non-elastic. Therefore, no visible extension appears in the string, but even in cases when this extension is noticeable, the string does not turn back to its original length, and as a result, it is considered as a non-elastic material. Therefore, the Hooke's Law cannot be used to calculate the value of tension.
Example 3
What is the minimum tension present in a rope if it is used to lift a 30 kg object? Take g⃗ = 9.81 m/s2.
Solution 3
The situation is described in the figure below.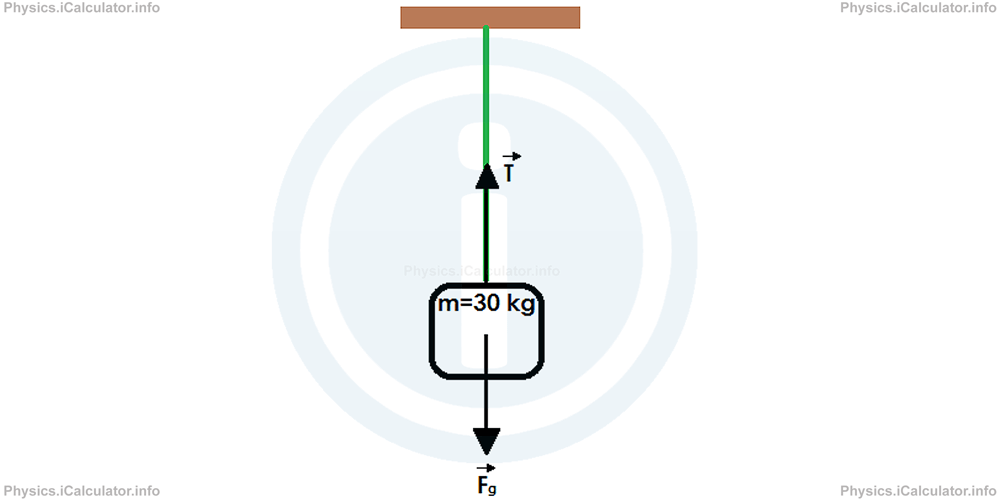
The minimum tension occurs when its value is equal to that of the gravitational force. Thus, we have
T⃗min = -F⃗g
= -m × g⃗
= -30kg × 9.81N/kg
= -294.3N
The sign minus means that the tension acts in the opposite direction of gravity.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 4.4.4 What is Tension?. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension), you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension) Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "What is Tension?" physics lesson? People who liked the "Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension) lesson found the following resources useful:
- Tension Definition Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this tension definition (see below)
- Dynamics Physics tutorial: Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension). Read the Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension) physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Dynamics
- Dynamics Revision Notes: Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension). Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension)
- Dynamics Practice Questions: Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension). Test and improve your knowledge of Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension) with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Dynamics questions with our excellent Dynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Dynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning dynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Newton's First Law of Motion. The Meaning of Inertia
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Types of Forces III (Elastic Force and Tension)" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.