Menu
Physics Lesson 9.1.4 - Auxiliary Units of Volume
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Auxiliary Units of Volume, this is the fourth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Fluids. Density of Fluids, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Auxiliary Units of Volume
As mentioned above, the units of volume change 1000 by 1000. Thus, jumping from one unit of volume into another using the SI system of units is a pretty hard task. It is like trying to climb the stairs which have very high steps as shown in the figure below.
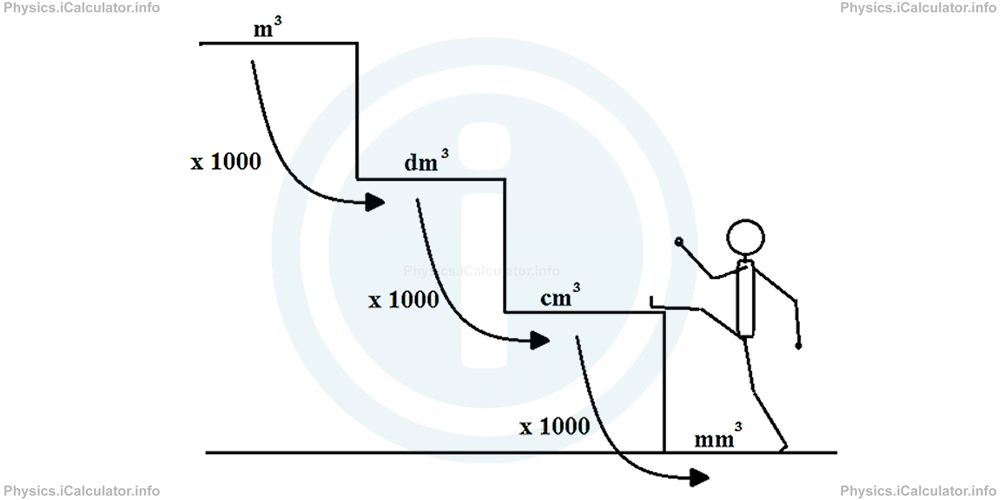
To avoid such issues, an auxiliary unit known as "Litre, L" is introduced. Litre is used only in fluids, i.e. to express the volume of liquids and gases. Litre is numerically equal to cubic decimetre (1 L = 1 dm3) but it offers an important advantage compared to standard SI units of volume: its multiples and sub-multiples change 10 by 10 instead of 1000 by 1000, facilitating a lot in this way the process of calculations. It is like building some auxiliary steps between the already built ones in the stairs shown in the figure above. Look at the figure.
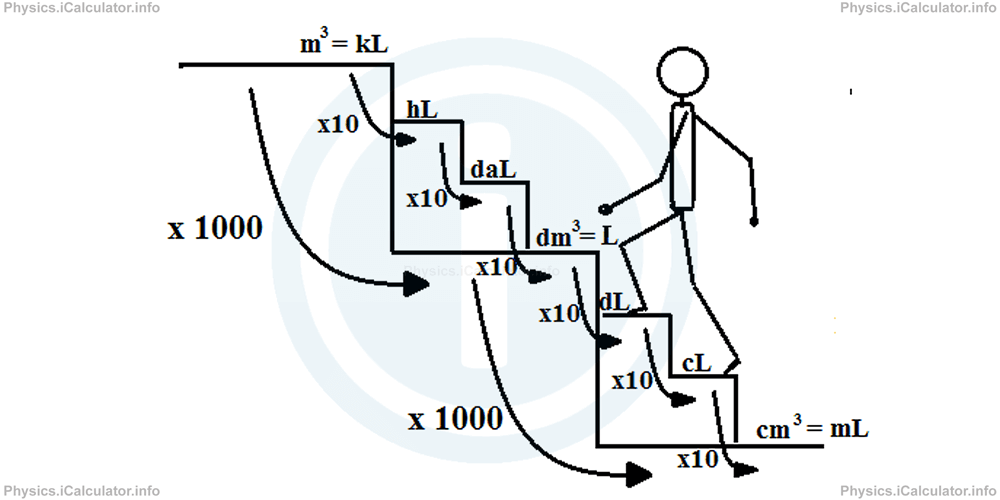
Remark! The auxiliary units of volume exist only for amounts we use in daily life, i.e. they extend from cm3 (mL) to m3 (kL). No auxiliary units exist out of this range.
Example 2
A graduated cylinder weighs 83.0 g when empty and 158.0 kg when 90 mL of an unknown liquid is poured in it. Calculate the density of liquid in kg/m3.
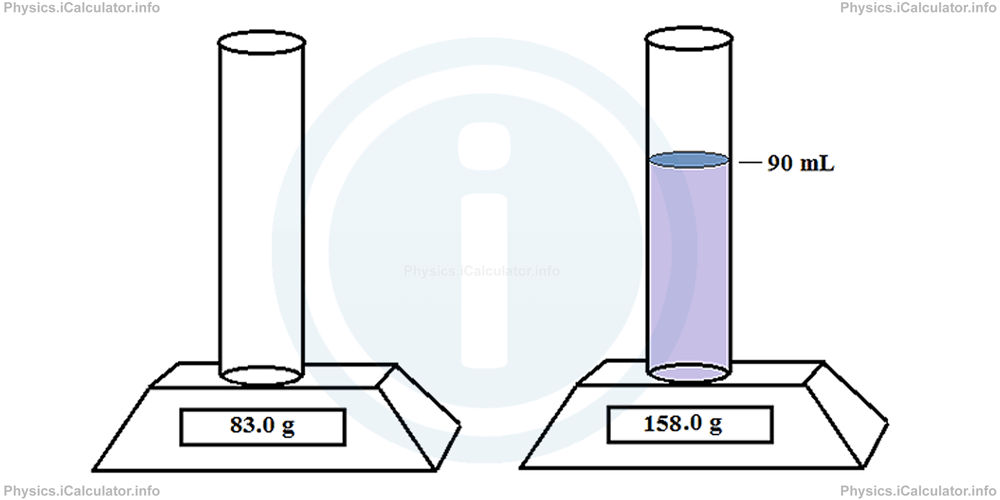
Solution 2
Mass of the liquid is obtained by subtracting the two values shown in the balance. Thus,
= 158.0 g - 83.0 g
= 75.0 g
The volume of liquid is written as 90 cm3 instead of 90 mL. Therefore, we obtain for density of liquid,
= 75.0 g/90 cm3
= 0.8 g/cm3
= 800 kg/m3
To calculate the density of a gas, we simply divide its mass with the volume of the whole container as gases fill up all the space of the closed container in which they are.
Example 3
An empty balloon weighs 4.6 g. Calculate the mass of balloon in grams after filling it with 4 L of air. Take the density of air equal to 1.3 kg/m3.
Solution 3
Given that
mempty ballon = 4.6 g
ρair = 1.3 kg/m3 = 0.0013 g/cm3
Vballoon = Vair = 4 L = 4000 mL = 4000 cm3
we obtain for mass of air
= 0.0013 g/cm3 × 4000 cm3
= 5.2 g
Therefore, the total mass of balloon after filling it with air is
= 4.6 g + 5.2 g
= 9.8 g
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 9.1.4 Auxiliary Units of Volume. There are 5 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Fluids. Density of Fluids, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Fluids. Density of Fluids Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Auxiliary Units of Volume" physics lesson? People who liked the "Fluids. Density of Fluids lesson found the following resources useful:
- Units Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this units (see below)
- Density and Pressure Physics tutorial: Fluids. Density of Fluids. Read the Fluids. Density of Fluids physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Density and Pressure
- Density and Pressure Revision Notes: Fluids. Density of Fluids. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Fluids. Density of Fluids
- Density and Pressure Practice Questions: Fluids. Density of Fluids. Test and improve your knowledge of Fluids. Density of Fluids with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Density and Pressure questions with our excellent Density and Pressure calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Density and Pressure Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning density and pressure - read our next physics tutorial: Pressure. Solid Pressure
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Fluids. Density of Fluids" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.