Menu
Physics Lesson 11.1.1 - What are Waves?
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on What are Waves?, this is the first lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
What are Waves?
As we know, everything in universe is in motion. Nothing can be considered as absolutely at rest. As discussed in the tutorial "Motion. Types of Motion", objects can perform linear, projectile, circular, elliptic and other types of motion. One of the most widespread types of motion is oscillatory (or vibrational) motion, which represents a kind of periodic motion, typical for waves. Obviously, this kind of motion needs the suitable conditions to take place such as its own medium, a source that generates the disturbance in the medium, etc., otherwise it is difficult to produce a sustainable oscillatory motion.
By definition, a wave is a regular disturbance on the medium (caused by a source), which travels through space and matter (i.e. through medium), transferring energy from one place to another.
If we split the sentence of the above definition in parts, we will observe three key concepts that need explication. They are:
1. Regular disturbance
Regular disturbance represents an alteration or displacement of a region of a medium from its equilibrium state. In waves, his alteration or displacement occurs in regular shapes and it is periodical, i.e. it repeats itself in equal intervals. For example, when you stretch a rope, it is in equilibrium. When you shake it, you cause a periodical disturbance in the rope and the surrounding air and as a result, the rope moves in regular periodical cycles like this
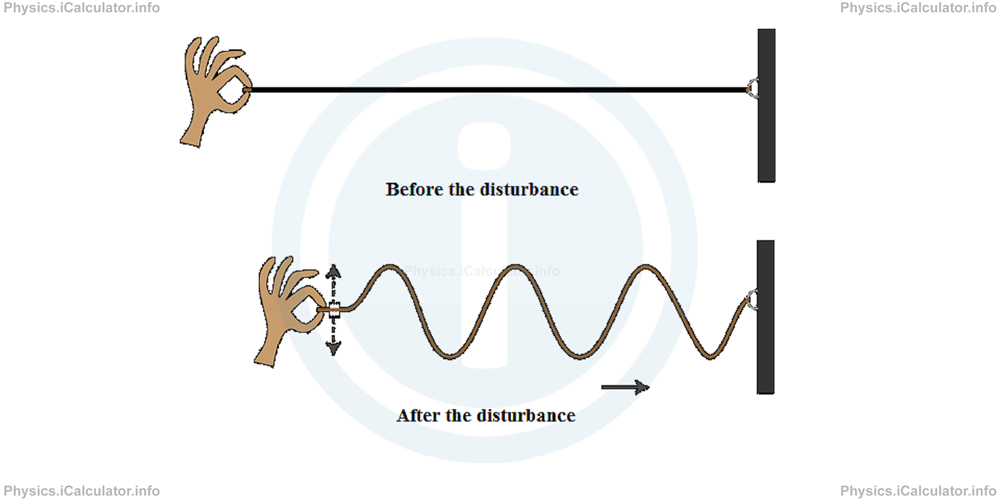
2. Medium of propagation
Medium of propagation represents any substance that allows the disturbance to propagate in other regions. In the above example, the medium of wave propagation is the rope, not the air, as the disturbance caused by the up-and-down shake of the hand, propagates along the rope.
3. Transferring energy
A wave transfers only energy, not matter. This is obvious, since the rope in the example above does not move from its place, it only shakes but it does not displaces horizontally. If we consider a certain piece of the rope, we can see that it moves only vertically. Only the disturbance shifts horizontally; this causes a wave to carry energy during its propagation. However, no matter is transferred throughout the wave. Indeed, if you throw a ball on seawater, it will move only up and down at the same place due to water waves if no external factors such as wind, any pushing force etc., are present as shown in the figure below.
In other words, we can define a wave as "a regular oscillation that shifts in space". In this sense, a wave is an extension of the concept of oscillations in SHM we discussed in the previous section.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 11.1.1 What are Waves?. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "What are Waves?" physics lesson? People who liked the "Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves lesson found the following resources useful:
- Definition Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this definition (see below)
- Waves Physics tutorial: Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves. Read the Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Waves
- Waves Revision Notes: Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves
- Waves Practice Questions: Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves. Test and improve your knowledge of Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Waves questions with our excellent Waves calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Waves Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning waves - read our next physics tutorial: General Equation of Waves
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Types of Waves. The Simplified Equation of Waves" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.