Menu
Physics Lesson 11.4.2 - Types of Interference
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Types of Interference, this is the second lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Interference of Waves, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Types of Interference
Interference may occur in all types of like waves. However, the interference pattern is more visible in transverse waves as the distinction between amplitude and wavelength is clearly observable in those waves because amplitude is perpendicular to wavelength. Therefore, we will focus only on transverse waves to explain the interference pattern and its properties.
Basically, there are two types of interference. They are:
1. Constructive Interference
In this kind of interference, waves enforce each other as they overlap at the same phase. We say the waves are coherent, i.e. they have the same behavior. As a result, we obtain a resultant wave whose amplitude is the arithmetic sum of the amplitudes of each single wave as shown in the figure below.
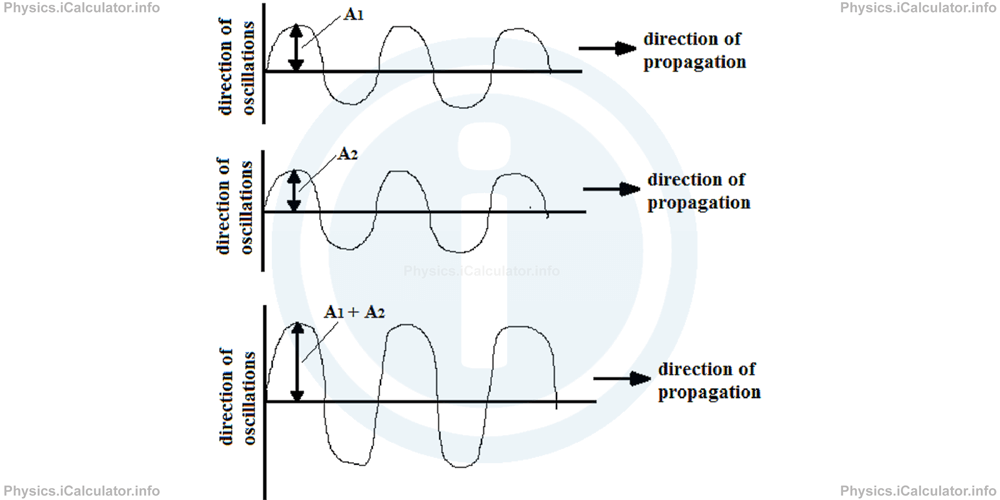
In this figure, the resultant wave has the same horizontal features (phase, wavelength, frequency, speed and period) as the two constituent waves but it has a greater amplitude as the waves overlap constructively. As a result, a stronger wave will be produced.
Mathematically, we can write for the resultant amplitude of the wave produced during a constructive interference:
As an example of constructive interference, we can mention the sound produced when you turn on two loudspeakers emitting the same song simultaneously. As a result, you will hear a louder volume if you are in between.
2. Destructive Interference
When two like waves have a phase shift of half a cycle, a destructive interference is produced, as shown in the figure below.
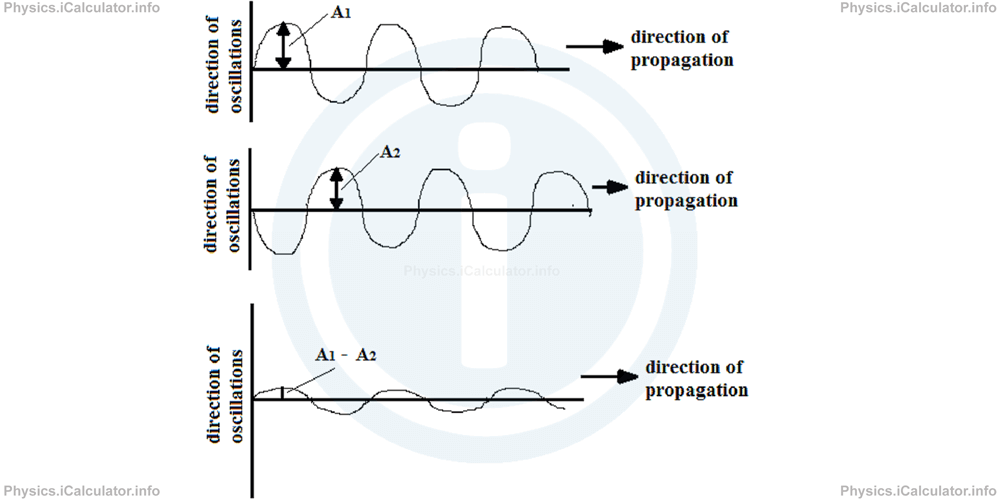
If we assume the first wave has a slightly greater amplitude than the second wave, we obtain for the resultant amplitude
In the special case when the amplitudes of the constituent values are equal, the resultant amplitude is zero and therefore, the waves cancel each other. As a result, no resultant wave will exist anymore.
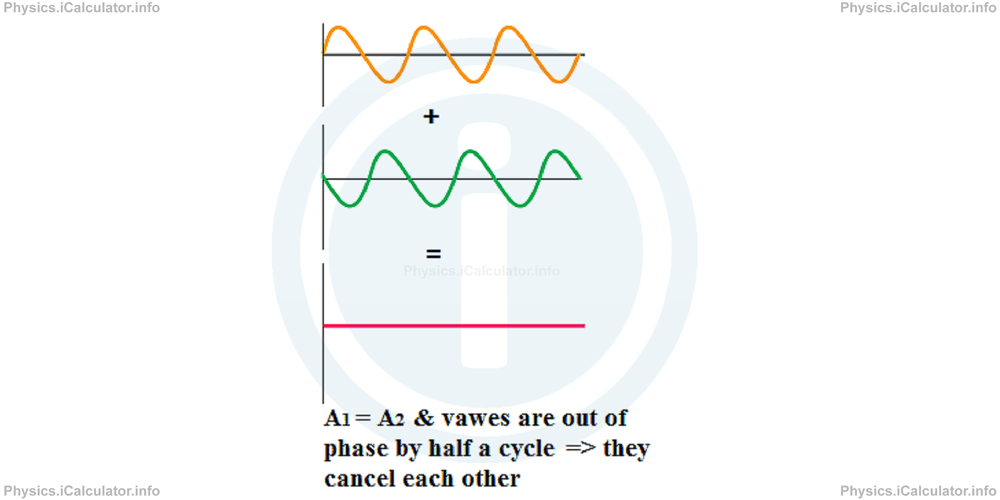
As an example of destructive interference, we can mention the modern electronic automobile muffler. It senses the sound propagating down the exhaust pipe and creates a matching sound with opposite phase. These two sounds interfere destructively, muffling the noise of the engine.
Example 1
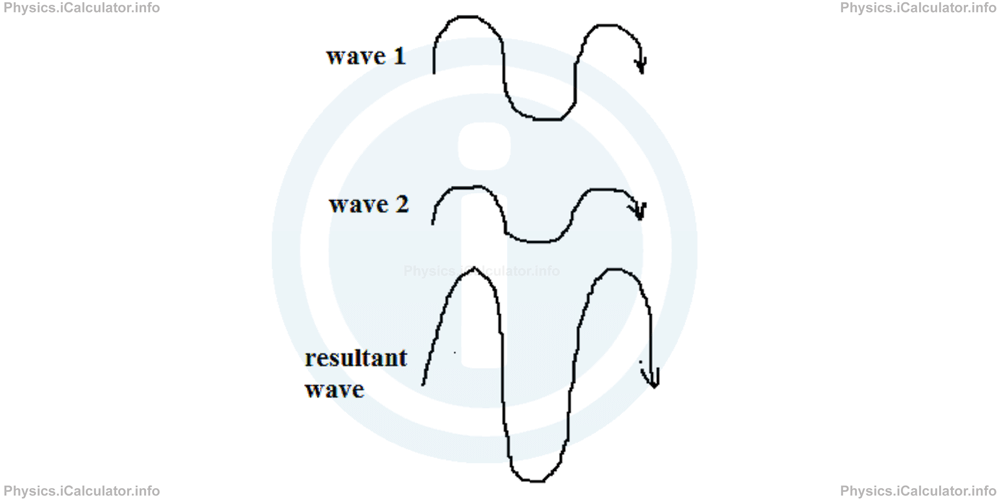
What is the amplitude of the resultant wave produced by interference in the following cases if the amplitude of the first wave is 12 cm and that of the second wave is 8 cm?
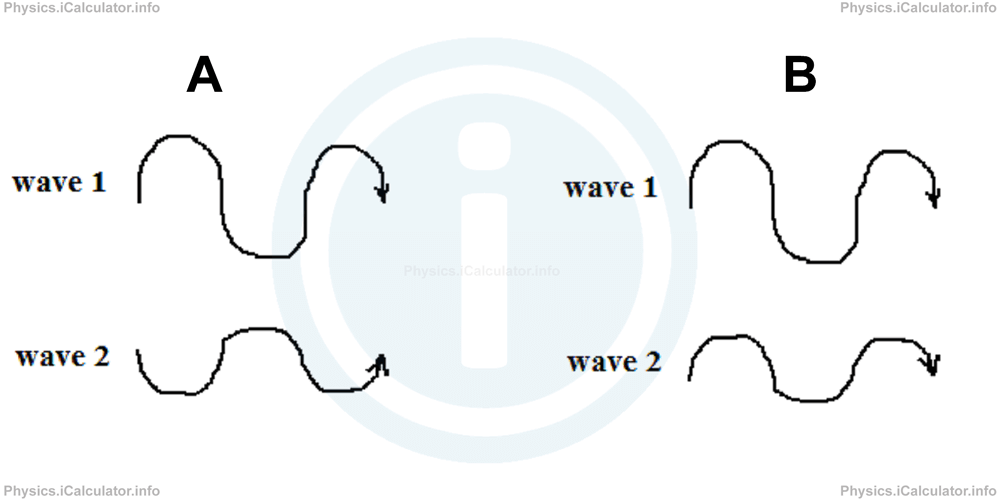
Solution 1
a) From the figure, we can see that waves are out of phase. Therefore, the resultant amplitude is
= 12 cm - 8 cm
= 4 cm
The shape of the resultant wave is:
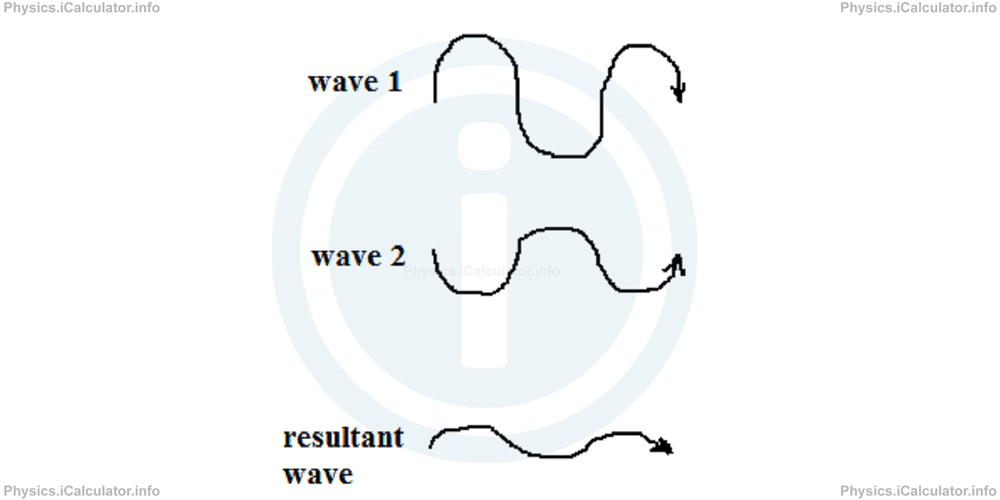
The resultant wave will be in phase with the wave which has the greater amplitude. In this case, it will be in phase with the first wave.
b) In this case, the interference is constructive because both waves have the same phase. Therefore, the resultant amplitude will be
= 12 cm + 8 cm
= 20 cm
As a result, a stronger wave with similar features will be produced, as shown in the figure.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 11.4.2 Types of Interference. There are 3 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Interference of Waves, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Interference of Waves Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Types of Interference" physics lesson? People who liked the "Interference of Waves lesson found the following resources useful:
- Category Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this category (see below)
- Waves Physics tutorial: Interference of Waves. Read the Interference of Waves physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Waves
- Waves Revision Notes: Interference of Waves. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Interference of Waves
- Waves Practice Questions: Interference of Waves. Test and improve your knowledge of Interference of Waves with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Waves questions with our excellent Waves calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Waves Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning waves - read our next physics tutorial: Sound Waves. Intensity and Sound Level
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Interference of Waves" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.