Menu
Physics Lesson 14.5.5 - The Relationship between Potential Difference and Electric Field
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on The Relationship between Potential Difference and Electric Field, this is the fifth lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Potential, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
The Relationship between Potential Difference and Electric Field
In the last two tutorials, we assumed the electric field between two parallel plates charged at opposite sign as uniform, especially when the distance d between the plates is small. As stated earlier, when we place a positive charge Q to the positive plate, its potential energy is at maximum. Thus,
For convenience, we can assume the potential at the negative plate as zero. As a result, the charge's potential energy at the negative plate is zero as well.
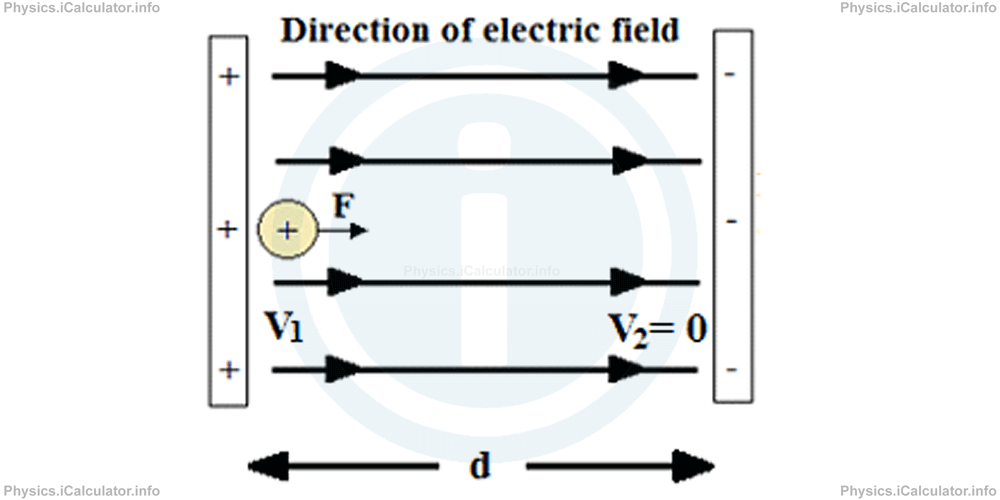
We know that the potential difference is
= EPE - 0/Q
= Q × E × d/Q
= E × d
If expressed in terms of E, the last formula becomes
From the above formula, we obtain the SI unit of electric field, which is Volt/metre [V/m], as the potential difference is measured in volts and distance in metres. Remember, in the previous tutorial we used another unit form electric field: Newton per Coulomb [N/C]. Hence, we can write
The reason why the standard unit of electric field is V/m and not N/C is because V/m contains one fundamental SI unit (metre), while neither Newton nor Coulomb are fundamental SI units.
The formula E = ΔV / d expresses how large the potential difference in the unit of charge must be in order to produce a given electric field. Thus, if in a given region the electric field is zero, the potential in that region does not change (is constant).
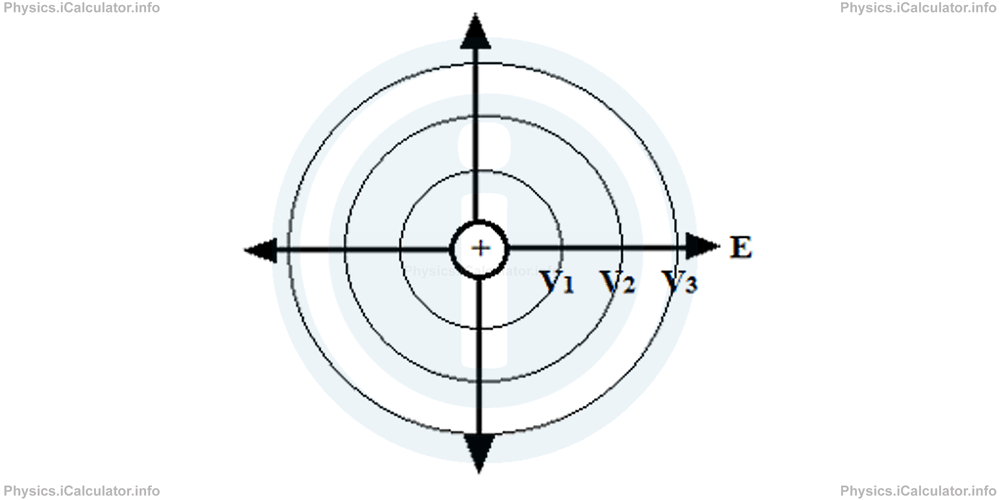
Electric potential decreases when we move in the direction of electric field. Thus, for a point charge as the one shown in the figure, we have V1 > V2 > V3.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 14.5.5 The Relationship between Potential Difference and Electric Field. There are 8 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Potential, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Potential Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "The Relationship between Potential Difference and Electric Field" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Potential lesson found the following resources useful:
- Field Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this field (see below)
- Electrostatics Physics tutorial: Electric Potential. Read the Electric Potential physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrostatics
- Electrostatics Revision Notes: Electric Potential. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Potential
- Electrostatics Practice Questions: Electric Potential. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Potential with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrostatics questions with our excellent Electrostatics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrostatics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrostatics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Flux. Gauss Law
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Potential" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.