Menu
Physics Lesson 14.4.2 - Electric Potential Energy of Point Charges
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Electric Potential Energy of Point Charges, this is the second lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Potential Energy, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Electric Potential Energy of Point Charges
The formula EPE = Q × E × d is true only in some specific cases, when the electric field is uniform (for example between two oppositely charged parallel plates). This is similar to the formula GPE = m × g × h which is true only when the object is inside a uniform gravitational field (near the Earth surface for example). However, the formula EPE = Q × E × d cannot be used for calculating the potential energy of a charge when it is placed inside the electric field of another point charge, as in this case the field is not uniform (it is greater near the charge location as the electric field lines are closer at that part). This is similar to when objects are at a considerable height from the ground, where we must use the standard formula of gravitational potential energy
Likewise, the calculation of elastic potential energy produced by a point charge reqires a similar formula, because the field is not uniform. Thus, from the similarities between gravitation and electrostatics, we can write k (or 1/4πϵ0) instead of G, Q1 and Q2 instead of M and m, and r instead of d in the formula of gravitational potential energy and obtain the corresponding formula for the electric potential energy produced by a point charge:
The only difference is that EPE can be both positive and negative, depending on the sign of charges involved, unlike the GPE, which is always positive.
Electric potential energy can be defined in terms of work done by the electric forces. For example, the electric potential energy of a system composed by two like point charges is equal to the work done by the electric force to move one of the charges from the distance r to infinity.
On the other hand, when the charges are of opposite sign, the electric potential energy is equal to the negative value of the work done by the electric force to move the charge - Q from the distance r to infinity. This is because at infinity the potential energy is zero, as the value of any number divided by infinity is zero. The graph below shows the electric potential energy as a function of distance for both like and unlike charges.
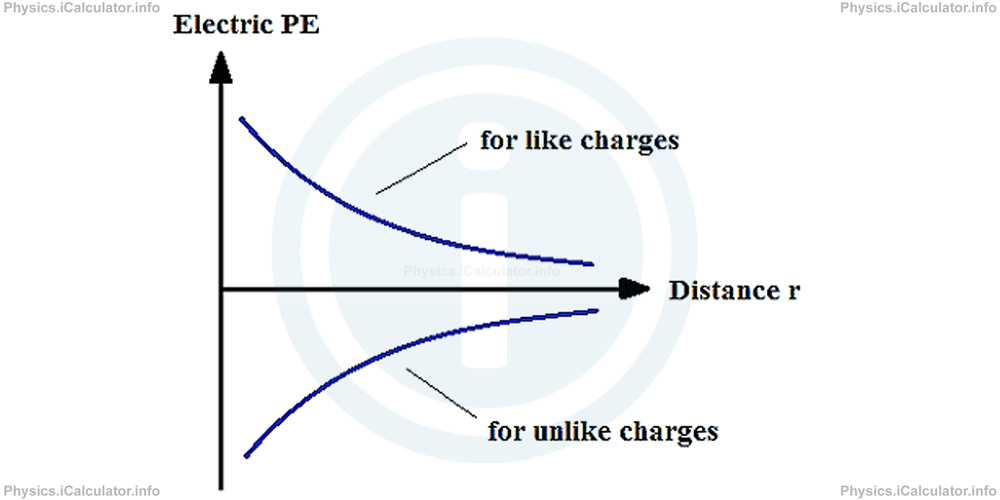
Obviously, in the figure there are the graphs of two different functions: one for two like charges and the other for two unlike charges. Both graphs are hyperbolae, as the variation between PE and r is of inverse type.
Example 2
Two point charges Q1 = 30 μC and Q2 = -20 μC are placed 2 m apart. How does the potential energy change if we increase the distance between charges to 6 m?
Solution 2
We can use the standard formula of electric potential energy
to calculate the potential energy between the two charges involved. Thus, giving that 30 μC = 3 × 10-5C and -20 μC = -2 × 10-5C we obtain after substitutions,
=-2.7 J
When the distance increases to 6 m, we obtain for the new electric potential energy:
= 9 × 109 × 3 × 10-5 × (-2) × 10-5/6
= -0.9 J
This means electric potential energy has increased as EPE of unlike charges increases when we separate them further.
We can use the same approach even when there are more than two charges, especially when they are not collinear. Let's consider an example in this regard.
Example 3
Three charges are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure.
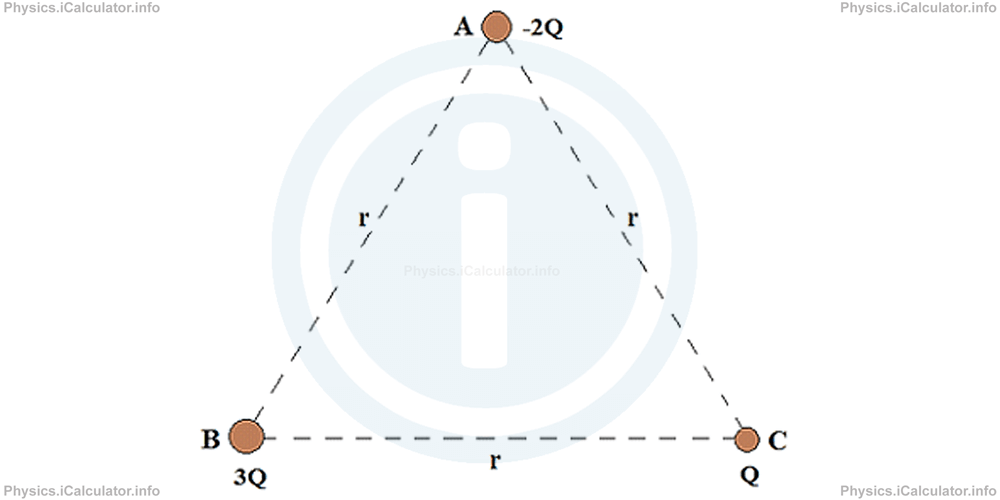
- What is the electric potential energy of the charge 3Q at the point B?
- What is the total electric potential energy of the system?
Solution 3
a) The potential energy of any charge at a given point is the algebraic sum of all individual potential energies due to each charge. No direction is involved, as potential energy is scalar. Thus,
EPEB = k × Qa × QB/raB + k × QC × QB/rCB
= k × Qa × QB + QC × QB/r
= k × -2Q) × 3Q + Q × 3Q/r
= k × -3Q2/r
b) The electric potential energy of system is the algebraic sum of each pair of potential energies. Thus,
= k × Qa × QB/rAB + k × QC × QB/rCB + k × Qa × QC/rAC
= k × Qa × QB + QC × QB + Qa × QC/r
= k × (-2Q) × 3Q + Q × 3Q + (-2Q) × Q/r
= k × -5Q2/r
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 14.4.2 Electric Potential Energy of Point Charges. There are 2 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Potential Energy, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Potential Energy Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Electric Potential Energy of Point Charges" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Potential Energy lesson found the following resources useful:
- Point Charges Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this point charges (see below)
- Electrostatics Physics tutorial: Electric Potential Energy. Read the Electric Potential Energy physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrostatics
- Electrostatics Revision Notes: Electric Potential Energy. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Potential Energy
- Electrostatics Practice Questions: Electric Potential Energy. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Potential Energy with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrostatics questions with our excellent Electrostatics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrostatics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrostatics - read our next physics tutorial: Electric Potential
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Potential Energy" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.