Menu
Physics Lesson 14.6.1 - The Meaning of Vector Area
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on The Meaning of Vector Area, this is the first lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Electric Flux. Gauss Law, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
The Meaning of Vector Area
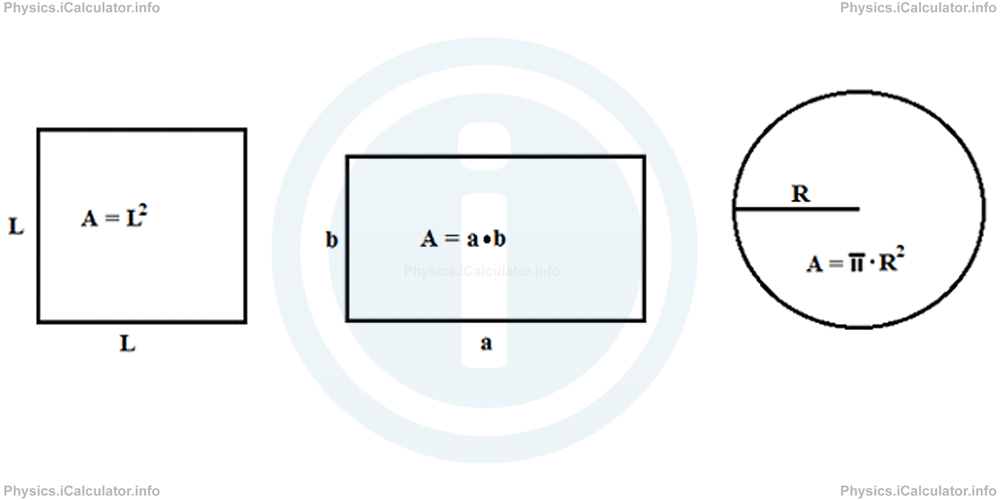
It is known from geometry that area is a scalar quantity, which represents the amount of surface enclosed within the boundary lines of a figure. Area is measured in square metres (m2). For example, the area of a square of side length L is L × L = L2, the area of rectangle of sides a and b is a × b, the area of a circle of radius R is π × R2 and so on.
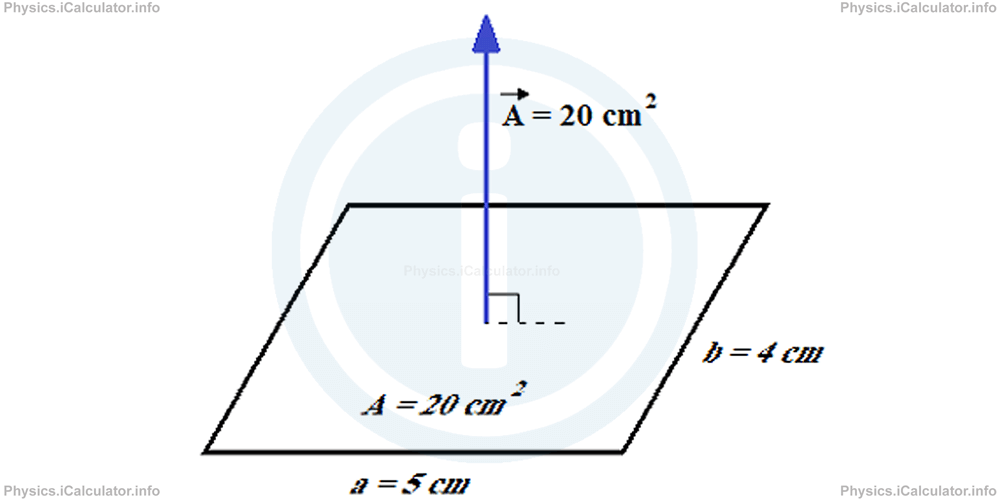
In some cases, it is convenient to appoint a vector to a given area, in order to make it operable with other vector quantities. This trick is especially common in electromagnetism. Thus, instead of writing the surface area as A square units, we consider the corresponding area vector of A⃗ units which is perpendicular to the given surface. For example, the vector area of a rectangle of side lengths a = 5 cm and b = 4 cm has a magnitude of A = 5 cm × 4 cm = 20 cm2 (20 units) and it is perpendicular to the plane of rectangle, as shown in the figure.
When area represents a positive quantity, the direction of its corresponding vector is in the outward direction, while when it represents a negative quantity, the corresponding vector is in the inward direction.
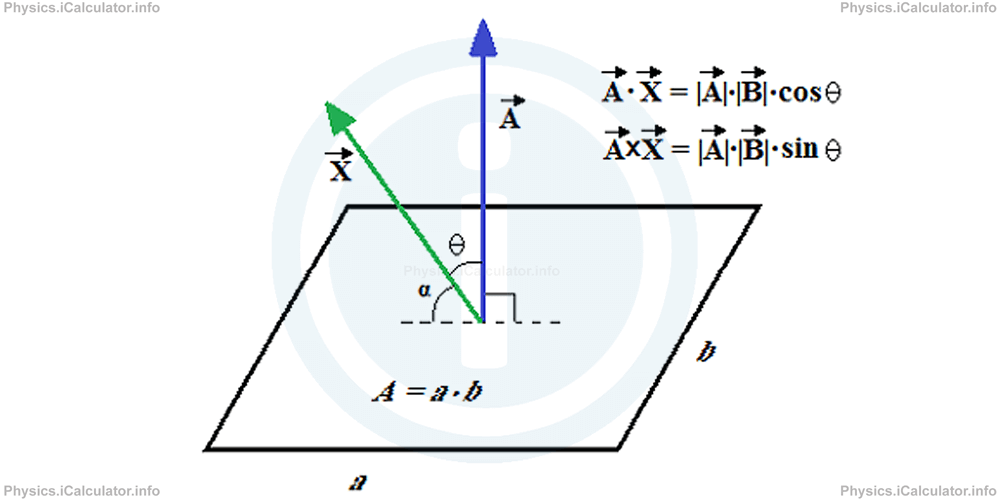
If another vector quantity is multiplied by a given area vector, we consider the angle between them as a part of multiplication. The introduction of area vector creates the possibility to apply both the dot and cross product of the two vectors, as needed. For example, if we have a vector quantity X which forms and angle θ to the area vector, as shown in the figure,
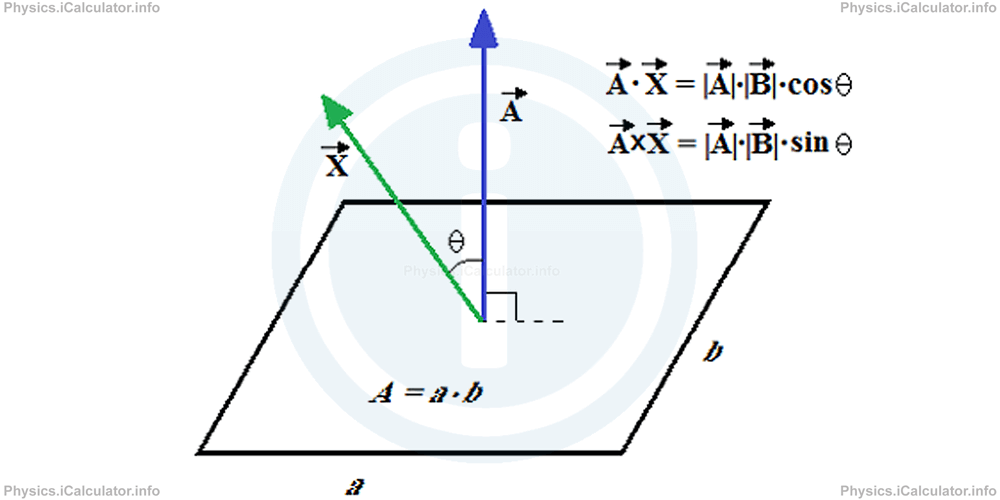
From the definition of the dot (scalar) product of two vectors, we have
and the cross (vector) product of the two given vectors (based on the definition of cross product of vectors) is
When the angle between the two vectors is not given but is given the angle α between the vector X and the surface, we consider the complementary angle θ = 90° - α during the operations.
Example 1
A vector V = 8 units forms an angle of 30° with the plane of a rectangle of dimensions 3 units and 5 units. The vector V extends in the outward direction. What is the magnitude of the cross product of the vector V and the area vector?
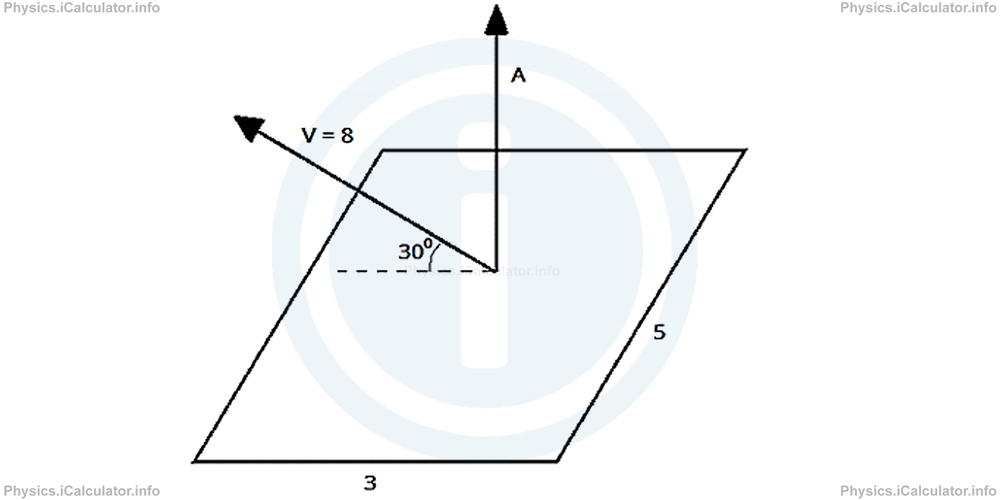
Solution 1
The area vector A is
The angle between the two vectors is
= 60°
The magnitude of cross product of A and V therefore is
= 8 × 15 × sin 600
= 8 × 15 × √3/2
= 60√3
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 14.6.1 The Meaning of Vector Area. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Electric Flux. Gauss Law, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Electric Flux. Gauss Law Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "The Meaning of Vector Area" physics lesson? People who liked the "Electric Flux. Gauss Law lesson found the following resources useful:
- Vector Area Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this vector area (see below)
- Electrostatics Physics tutorial: Electric Flux. Gauss Law. Read the Electric Flux. Gauss Law physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Electrostatics
- Electrostatics Revision Notes: Electric Flux. Gauss Law. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Electric Flux. Gauss Law
- Electrostatics Practice Questions: Electric Flux. Gauss Law. Test and improve your knowledge of Electric Flux. Gauss Law with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Electrostatics questions with our excellent Electrostatics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Electrostatics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning electrostatics - read our next physics tutorial: Capacitance and Capacitors
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Electric Flux. Gauss Law" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.