Menu
Physics Lesson 13.9.3 - Relationship between Volume and Temperature at Constant Pressure. The Charles's Law
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
Welcome to our Physics lesson on Relationship between Volume and Temperature at Constant Pressure. The Charles's Law, this is the third lesson of our suite of physics lessons covering the topic of Gas Laws, you can find links to the other lessons within this tutorial and access additional physics learning resources below this lesson.
Relationship between Volume and Temperature at Constant Pressure. The Charles's Law
If we supply some heat energy to the ideal gas inside the cylinder of the previous paragraphs by allowing the piston to slide freely up or down (here, up), we obtain a process at constant pressure as it is self-regulated automatically in order to balance the atmospheric pressure which acts from above the piston.
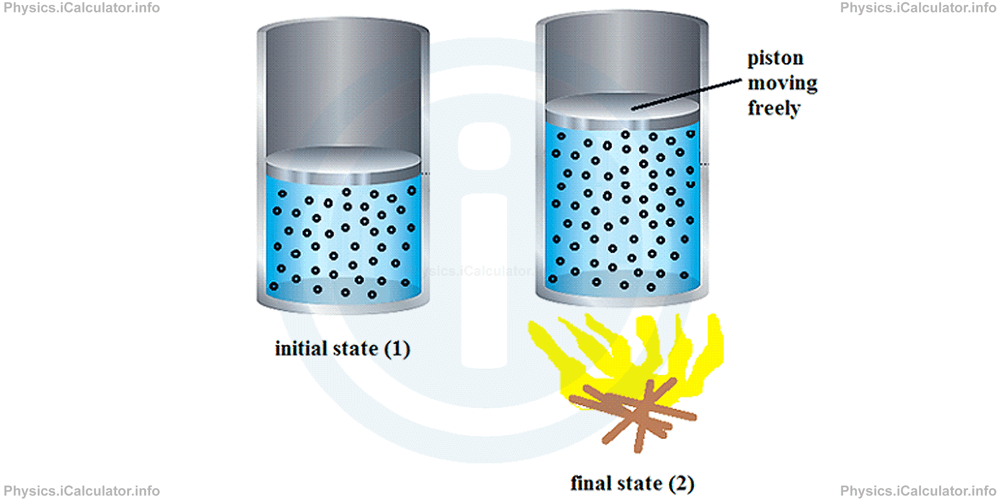
Such a process - which occurs at constant pressure - is known as isobaric process. We write P1 = P2 = P. If we apply again the ideal gas law for the two states 1 and 2, we obtain
for the initial state and
for the final state of the gas, where n is the number of moles and R is the ideal gas constant (both remain unchanged during the entire process).
Dividing both equations side by side, we have
Or
The above equation is known as the Charles's Law.
The corresponding P - V graph for an isovolumetric process is shown below.
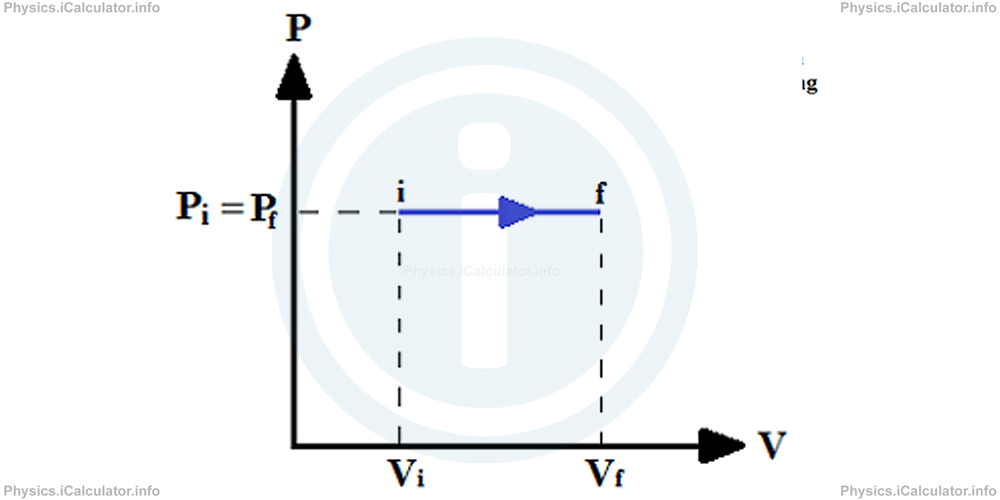
The area under the graph represents the work done by the gas to lift the piston, as explained in the previous tutorial.
Example 4
An ideal gas contracts at constant pressure from 8 L to 3 L when some heat energy is taken off from it. As a result, the gas temperature becomes -3°C at the end of process. What w the initial temperature of gas in Celsius degree?
Solution 4
We have the following clues:
P1 = P2 = P
V1 = 8 L = 0.008 m3
V2 = 3 L = 0.003 m3
T2 = - 23°C = - 3 + 273 = 270 K
T1 = ?
Since this is an isobaric process, we apply the Charles's Law to find the initial temperature of gas. We have
0.008 m3/0.003 m3 = T1/270 K
T1 = 0.008 m3 × 270 K/0.003 m3
= 720 K
When converted into Celsius scale, this value becomes 720 - 273 = 447°C.
You have reached the end of Physics lesson 13.9.3 Relationship between Volume and Temperature at Constant Pressure. The Charles's Law. There are 4 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Gas Laws, you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below.
More Gas Laws Lessons and Learning Resources
Whats next?
Enjoy the "Relationship between Volume and Temperature at Constant Pressure. The Charles's Law" physics lesson? People who liked the "Gas Laws lesson found the following resources useful:
- Charles Feedback. Helps other - Leave a rating for this charles (see below)
- Thermodynamics Physics tutorial: Gas Laws. Read the Gas Laws physics tutorial and build your physics knowledge of Thermodynamics
- Thermodynamics Revision Notes: Gas Laws. Print the notes so you can revise the key points covered in the physics tutorial for Gas Laws
- Thermodynamics Practice Questions: Gas Laws. Test and improve your knowledge of Gas Laws with example questins and answers
- Check your calculations for Thermodynamics questions with our excellent Thermodynamics calculators which contain full equations and calculations clearly displayed line by line. See the Thermodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™ below.
- Continuing learning thermodynamics - read our next physics tutorial: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
Help others Learning Physics just like you
Please provide a rating, it takes seconds and helps us to keep this resource free for all to use
We hope you found this Physics lesson "Gas Laws" useful. If you did it would be great if you could spare the time to rate this physics lesson (simply click on the number of stars that match your assessment of this physics learning aide) and/or share on social media, this helps us identify popular tutorials and calculators and expand our free learning resources to support our users around the world have free access to expand their knowledge of physics and other disciplines.
Thermodynamics Calculators by iCalculator™
- Carnot Engine Efficiency Calculator
- Entropy Calculator
- Gas Laws Calculator
- Molecular Mean Free Path Calculator
- Translational Kinetic Energy Of Gas Calculator
- Root Mean Square Speed Calculator
- Ideal Gas Law Calculator
- Change In The Gas Internal Energy Calculator
- Radiative Heat Transfer Calculator
- Evaporative Heat Transfer Calculator
- Convective Heat Transfer Calculator
- Conductive Heat Transfer Calculator
- Final Temperature Of Mixture Calculator
- Heat Absorbed Or Released Calculator
- Thermal Expansion Calculator
- Temperature Calculator